Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
2
COMMON DISEASES OF PERENNIAL
FRUIT CROPS
ANTHRACNOSE
■
Anthracnose refers to a group of fungal diseases
characterised by the development of dark, sunken spots or
lesions, often with a raised rim, on affected foliage, stems
and fruit. Under warm, humid conditions, the surface of
the lesion is covered by a sticky pink spore mass (conidia)
produced in a fungal fruiting body termed an acervulus.
Cause
Fungi belonging to several genera cause anthracnose
diseases. These include
Diplocarpon
(black spot of roses),
Elsinoe
(anthracnose or black spot of grape) and, in
particular, species of
Colletotrichum
. Anthracnose diseases
caused by
C. gloeosporioides
are a major cause of loss in
many tropical fruit crops.
Although the fungus has a teleomorph or sexual stage -
Glomerella cingulata -
this plays only a minor role in the
disease cycle and it is
C. gloeosporioides
, the anamorph or
asexual stage of the fungus, which causes anthracnose
diseases.
Fig 2.1 The distinct, concave shape of an anthracnose lesion on
persimmon skin.
Fig 2.3 A germinated spore of
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
on papaya skin showing a germ tube and an appressorium.
Inset: spores.
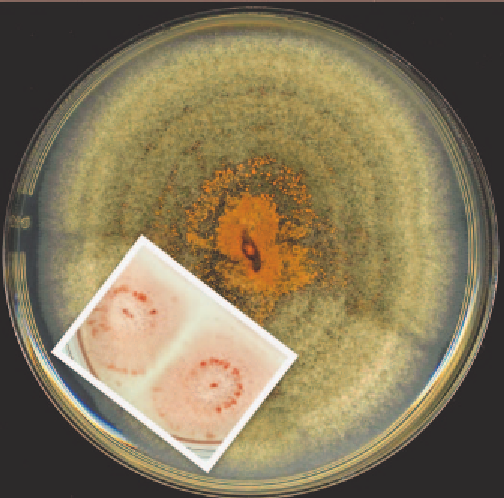
Fig 2.2 Cultures of
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
and
C. acutatum
(inset).