Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
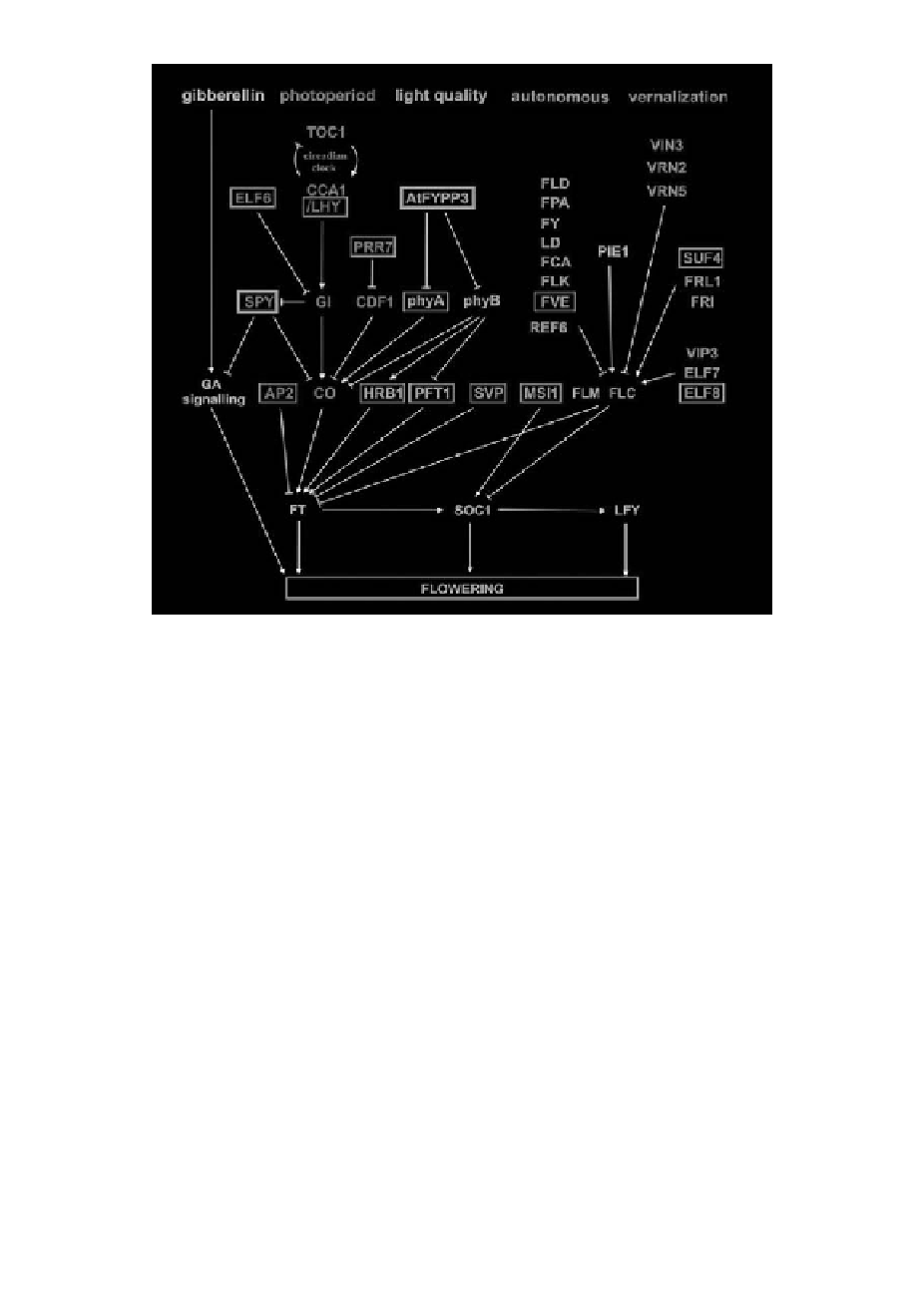
Figure 2.
A simplified chart showing Arabidopsis flowering pathways and corresponding gene homologs in
Fragaria.
Gene homologs
found in cDNA libraries produced from SD and EB genotypes are surrounded by blue and red
boxes, respectively. Arrows indicate positive regulation and bars negative regulation.
Most genes of the Arabidopsis photoperiodic pathway were found also in
Fragaria, and some of the lacking genes were present among Rosaceae ESTs (Table
2). We found several genes encoding putative Fragaria photoreceptor apoproteins
including phyA, phyC, cry2, ZTL (ZEITLUPE) and FKF1 (FLAVIN BIND-
ING KELCH REPEAT F-BOX 1) [43]. Of the central circadian clock genes,
homologs of LHY and TOC1 [5,7] were present in our EST libraries and GDR,
respectively, but CCA1 [6] was lacking from both Fragaria and Rosaceae data-
bases. Furthermore, a putative Fragaria CO from the flowering regulating output
pathway has been cloned earlier [44]. Among the regulators of CO transcrip-
tion and protein stability, GI (GIGANTEA) [45] was identified from Rosaceae
and putative COP1, SPA3 and SPA4 [46,47] from Fragaria. In addition to genes
of the photoperiodic pathway, homologs for both known sequences belonging
to light quality pathways, PFT1 (PHYTOCHROME AND FLOWERING
TIME 1) and HRB1 (HYPERSENSITIVE TO RED AND BLUE 1) [48,49],
were found from our EST libraries.