Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
content was greatly reduced in the young flower buds of the quadruple Q3 mu-
tant whereas was restored in the penta mutant when compared to that in the WT
and opr3 mutant (Figure 6D).
GA Application Induces DAD1 Expression Prior to the
Induction of MYB21, MYB24, and MYB57
DAD1 is a stamen specific gene encoding chloroplastic phospholipase A1 protein
that catalyzes the first step of JA biosynthesis. Mutation in DAD1 resulted in a
typical JA-deficient phenotype in stamen development [40], a phenotype similar
to that of myb21-t1 myb24-t1 double mutant. As mentioned earlier, JA likely acts
downstream of GA to regulate the expression of MYB21, MYB24 and MYB57.
To study whether there is a correlation between GA-regulated DAD1 expression
and MYB21, MYB24 and MYB57 expression, we treated the ga1-3 gai-t6 rga-t2
rgl1-1 quadruple mutant with GA. We first confirmed the GA-responsiveness
in the quadruple mutant plants by examining the expression of known GA-re-
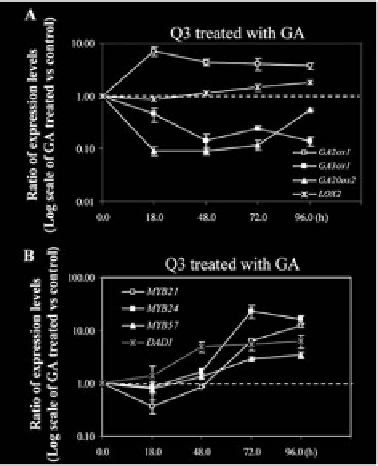
sponse genes GA3ox1, GA20ox2 and GA2ox1 (Figure 7A). Then we examined
the expression of DAD1 and the three MYB genes MYB21, MYB24 and MYB57.
Figure 7.
GA Induces DAD1 Expression Prior To Induction of Expression of MYB21, MYB24, and MYB 57.
(A-B) Semi-quantitative
analysis of LOX2, GA2ox1, GA3ox1 and GA20ox2 (A), DAD1 (in red line), MYB21,
MYB24 and MYB57 (B) expression in the ga1-3 gai-t6 rga-t2 rgl1-1 (Q3) mutant flowers at 18, 48, 72 and 96
hrs after GA treatment. Data were averaged from 2-4 batches of independently treated samples and ACTII was
used as the normalization control. The graph was drawn based on Log10 scale of the ratio of the expression levels
of GA treated versus untreated samples.