Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
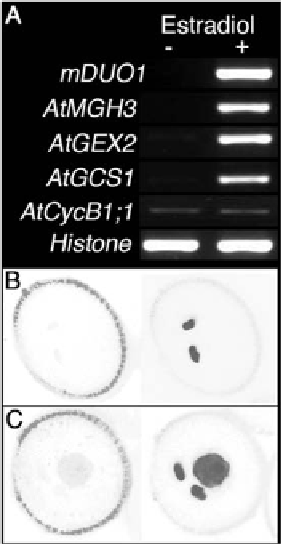
To independently confirm the regulation of germline genes by DUO1 we
ectopically expressed DUO1 in seedlings, and in pollen vegetative cells, where At-
MGH3, AtGEX2 and AtGCS1 are not normally expressed. As DUO1 contains a
recognition site for microRNA159 we used a resistant DUO1 cDNA (mDUO1)
with an altered nucleotide sequence at the miR159 binding site, but encoding
the native amino acid sequence [21]. Transgenic seedlings in which the mDUO1
cDNA was placed under the control of an estradiol inducible promoter [22]
showed mDUO1 induction when exposed to estradiol (Figure 2A). Expression
of the male germline genes, AtMGH3, AtGEX2 and AtGCS1, was also induced,
with high levels of transcripts present only in plants exposed to estradiol and
containing mDUO1 (Figure 2A). Similarly, when a DUO1::mRFP fusion was
ectopically expressed in pollen vegetative cells using the LAT52 promoter [23],
we observed ectopic expression of the AtMGH3 marker in vegetative cell nuclei
(Figure 2B,C). Thus ectopic expression of DUO1 is sufficient for activation of
germ cell-specific gene expression in a range of non-germline cells.
Figure 2.
Ectopic expression of DUO1 results in expression of male germline specific genes.
(A) RT-PCR
analysis of mDUO1, AtMGH3, AtGEX2, AtGCS1 and AtCycB1;1 expression in whole seedlings
transformed with the mDUO1 cDNA (see methods) under the control of an estradiol inducible promoter grown
on media without estradiol (−) or with estradiol (+). Histone H3 was used as a control. (B, C) Mature pollen grains
showing AtMGH3-H2B::GFP expression specifically in sperm cells in the absence of LAT52-DUO1::mRFP
(B), or in both the vegetative cell nucleus and sperm cells in the presence of LAT52-DUO1::mRFP (C). Left and
right panels correspond to RFP and GFP signals viewed by CLSM.