Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
sporophytic tissues of the ovules surrounding the embryo sac. In case of
AT4G12410, we did not detect expression in the wild-type pistils. For the other
four genes, the spatial expression patterns in the wild-type ovule and carpel tissues
were comparable to that in coa, but the expression levels were far lower than in
the mutant (data not shown). In summary, we provide evidence that a significant
fraction of the sporophytic transcriptome can be modulated by the presence or
absence of an embryo sac.
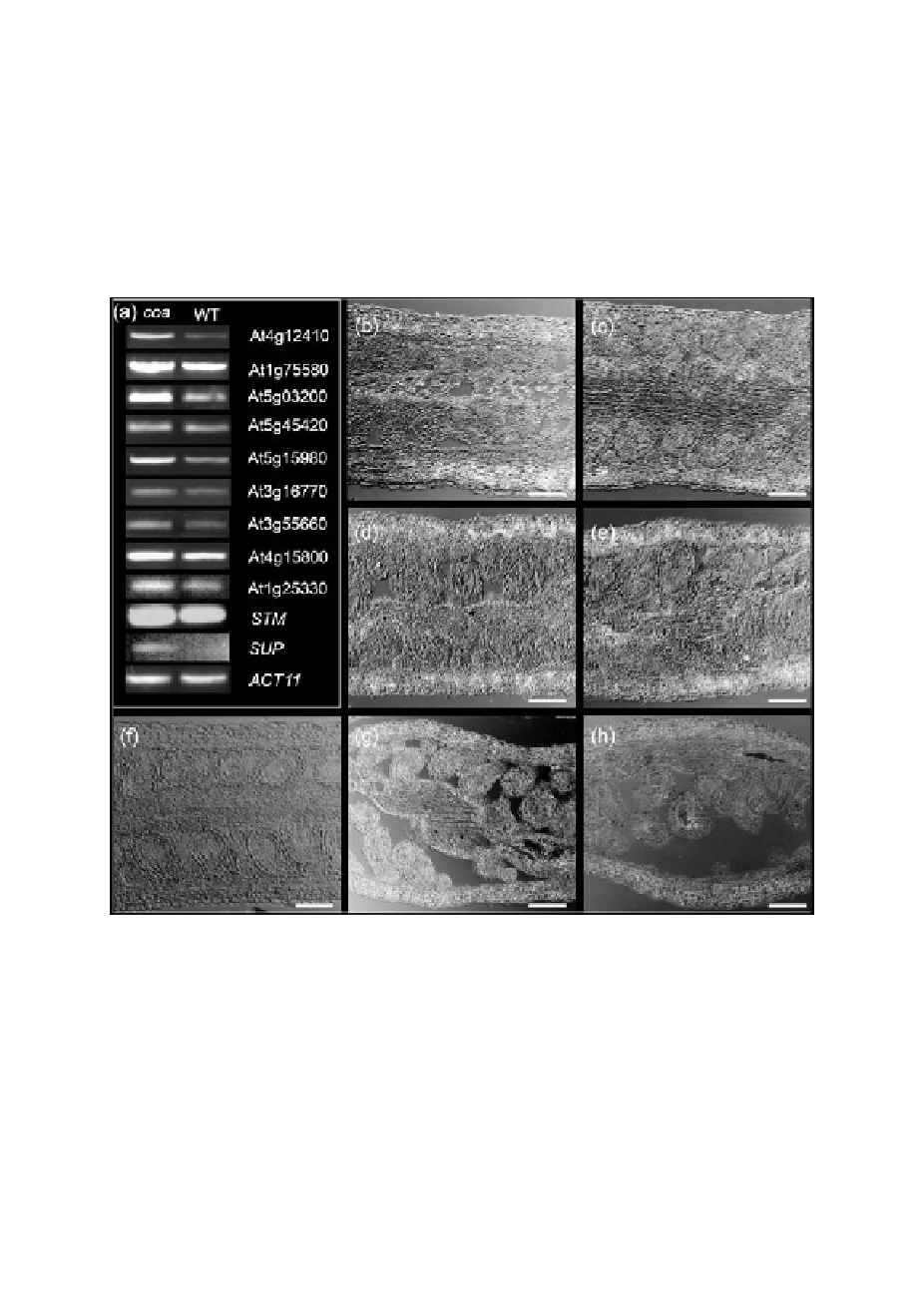
Figure 6.
Gain of expression in the sporophyte in the absence of a functional embryo sac: expression analysis in
the coatlique (coa) mutant.
(a) RT-PCR
for 11 genes in coa and wild-type (WT) pistils. Equal loading of both coa and WT cDNA templates
in PCR was monitored by expression of ACT11. SUP, SUPERMAN. Also shown are in situ expression patterns
of the following genes in coa pistil tissues: (b) AT4G12410, encoding an auxin-responsive Small Auxin Up RNA
(SAUR) protein; (c) AT1G75580, encoding an auxin-responsive protein; (d) AT5G03200, encoding a C3HC4-
type RING finger protein; and (e) at5g15980, encoding a PPR repeat containing protein. The corresponding
sense control probes did not show any expression (data not shown). (f ) AT4G12410 did not show any detectable
expression pattern in wild-type pistils. The other four genes exhibited spatial expression patterns in the wild-type
ovule and carpel tissues comparable to that of coa, but their wild-type expression levels were much lower than
in coa (data not shown). (g) We initially identified the over-expression of STM in the ovule tissues of spl (sensu
microarray data), and confirmed that this gene is over-expressed in the carpel and ovules of coa as well (panels a
and g). (h) A comparable but less intense spatial expression pattern of STM was seen in wild-type pistils. Scale
bars: 100
µ
m in panels b to h.