Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
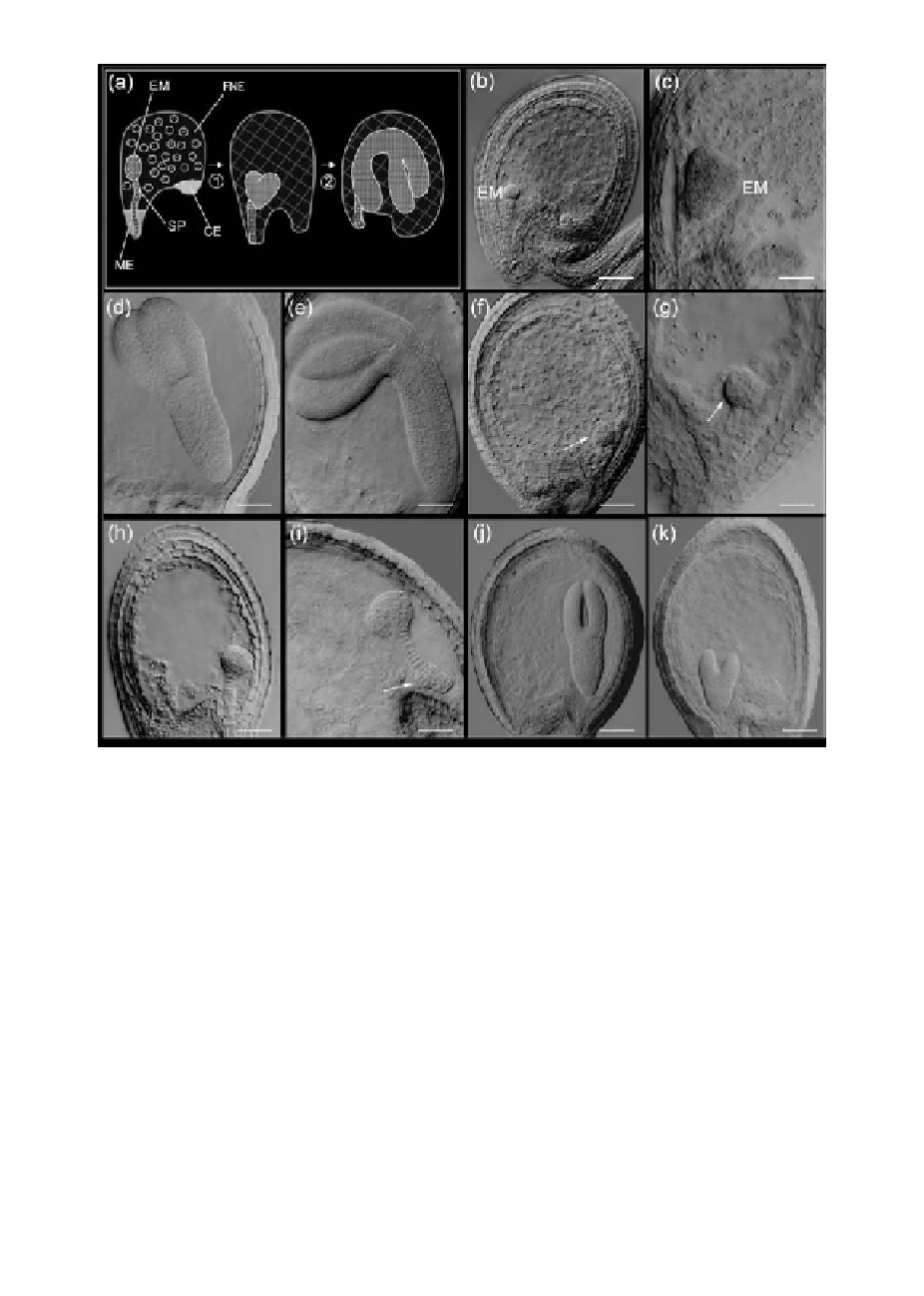
Figure 5.
Mutants arrested late in seed development.
(a) Shown
is a scheme of seed development in Arabidopsis. A globular embryo (EM) develops into heart stage
(1). Note that the peripheral endosperm nuclei surrounding the globular embryo are organized into three distinct
domains: micropylar endosperm (ME), chalazal endosperm (CE), and free nuclear endosperm (FNE). Following
rapid cellularization of endosperm, a torpedo stage embryo and then an upturned-U stage embryo is formed (2).
(b-e) Morphology of wild-type seed development corresponding to representative events described above. (f )
In oma-1 the embryo arrested at the mid-globular stage. The size of cells in embryo and endosperm were larger
than that in (g) the wild type. (h,i) In fey-1 the embryo arrested at around the late globular stage. Note that the
cells of the embryo and suspensor were large, and the suspensor displays a bend due to the irregularly bulged
cells (panel i, arrow). (j) The majority of the ila-1 embryos arrested when they were at upturned U stage. (k) A
small fraction of late-heart ila-1 embryos could also be observed. Scale bars: 10
µ
m for panels b, f, h, j, and k;
and 20
µ
m for panels c, d, e, g, and i.
Transcription Factors, Homeotic Genes, and Signaling
Proteins are Over-Expressed in the Absence of an Embryo Sac
Even though the two mutants we used in this study exhibit morphological-
ly normal carpels and ovules in the absence of an embryo sac, we considered
whether the gene expression program within the sporophyte is altered. The genes