Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 20.1
Continued
Transition
state (see
Figure 20.3)
Description of invasion impacts
Key disturbance
variables
Key response
variables
4
- Alternative stable state maintained by positive
feed-backs in nutrient cycling and fi re intensity
that promote the invader and other weedy
species over native species; herbaceous
understorey also makes frequent fi res possible
- Clearance of the
Acacia
in this advanced state
will result in weedy and secondary alien
species dominating the community. Old fi elds
with similar composition are maintained as
weedy herbaceous systems by indigenous
fossorial mammals, adding a further level of
positive feedback
(Authors' personal observations, and Holmes
2008)
Intensifi cation of all
key disturbance
variables
After
Acacia
clearance,
density of fossorial
mammals (molerats
and gerbils) intensifi es
* Data for
Acacia cyclops
which is of similar stature to
A. saligna
.
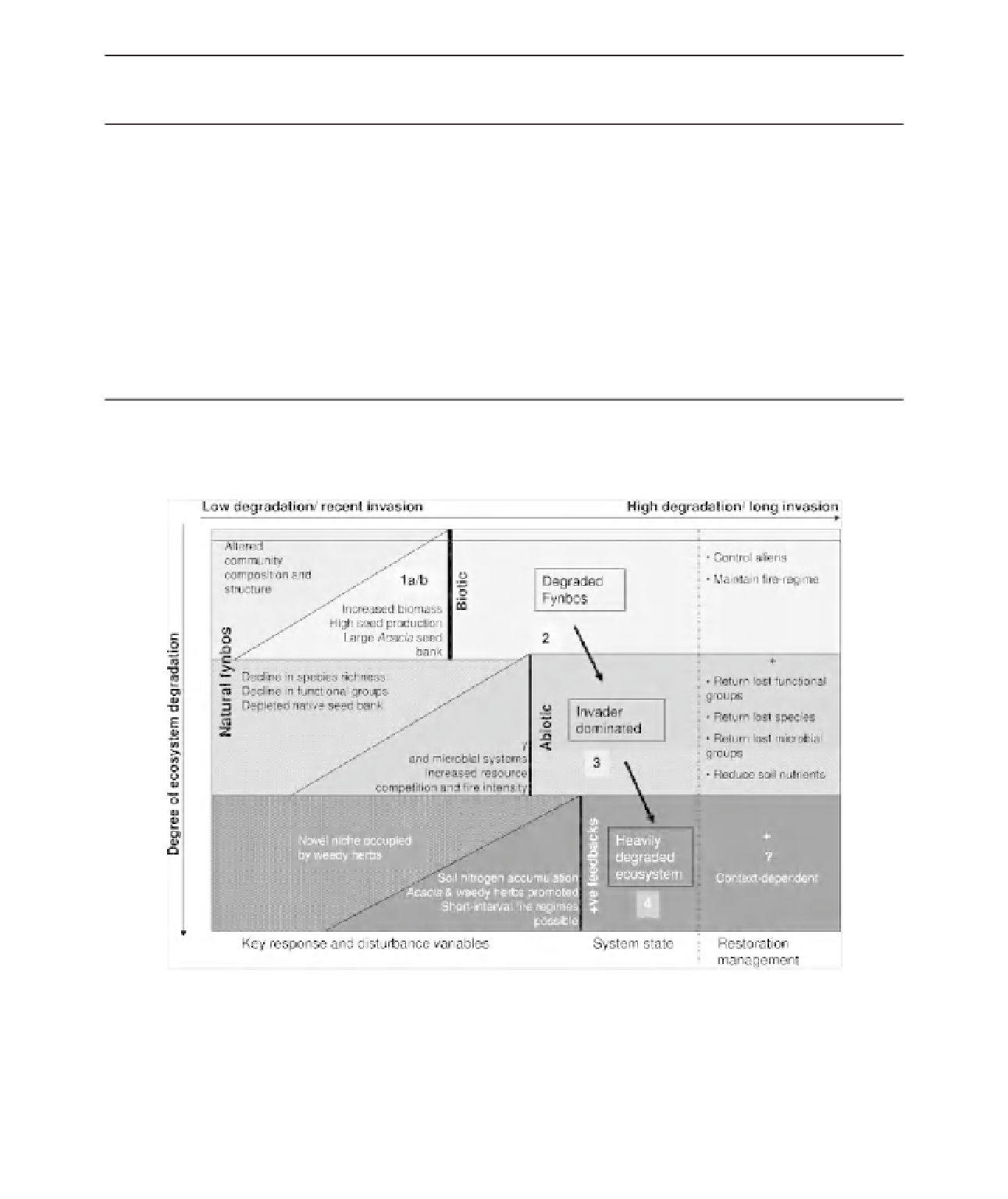
Figure 20.3
Acacia saligna
invasion of fynbos illustrating different ecosystem states and thresholds as invasion intensifi es.
The triangles represent invasion impacts by alien
Acacia
and the disturbance variables that lead to each system state; the
matrix represents the fynbos ecosystem and its response variables. Thresholds are indicated by the thick black lines.
Appropriate management actions to restore the ecosystem are listed in the right-hand column.