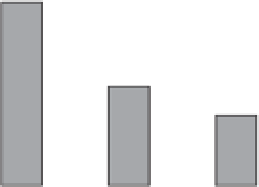Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
when emissions of SO
2
and NO
x
peaked. By the mid-
1980s, there was a perceptible decrease in emissions
(Mason 2002). By the year 2000, two thirds of surface
waters in Europe, where long-term monitoring
(n = 56) had been carried out, showed reductions in
acid deposition. Additionally, modelling studies of acid-
ifi cation in Norwegian surface waters indicate that
these waters will continue to recover slowly (Larssen
et al
. 2010). By 1983, almost all countries had com-
mitted to reduce their SO
2
emissions by 30% within a
decade, and to decrease by 70-80% by 2010 (United
Nations 1994). However, contrary to these emission
reductions, the NO
x
emissions have tended to increase,
for example in the United Kingdom. Therefore, acidifi -
cation related to N is still a grave problem.
Liming is the most common technique for restoring
acidifi ed lakes, for example in Scandinavian countries,
the United Kingdom (Scotland and Wales) and eastern
Canada. Limestone, which includes calcite (CaCO
3
)
and powdered dolomite, is the most commonly used
compound. Also, quicklime (CaO) and slaked lime
(Ca(OH)
2
) have been used in addition to alum
((Al
2
SO
4
)
3
· 14H
2
O). Liming produces longer lasting
buffering effects and pH generally does not rise above
7.0. The liming of Loch Fleet, Galloway, southwest
Scotland, facilitated the introduction and sustenance
of a trout population.
Both in Sweden and in Norway, large-scale liming is
used as a national strategy for preserving species
threatened by acidifi cation (Henrikson & Brodin 1995).
In Sweden alone, between 7500 and 11 000 km of
streams were limed annually to raise the pH to > 6.0 in
order to help indigenous fauna and fl ora to survive.
Nearly 90% of the acidifi ed bodies of surface water
have thus been restored.
25
a
20
15
b
10
b
5
0
Cyanobacteria
Other phyto-
plankton
Detritus
Figure 18.8
Clearance rates of adult zebra mussels
(
Dreissena
) on different food particles from Lake Zwemlust,
the Netherlands. The clearance rates on cyanobacteria are
signifi cantly higher than those on other phytoplankton and
detritus as indicated by the letters a and b above the bars.
(From Dionisio Pires
et al
. 2004. Reproduced by permission
of Blackwell Publishing.)
Dutch lakes the areas colonized by zebra mussels are
clearer, even to the naked eye, than the other lake parts.
In contrast to the practice in some European coun-
tries, in North America, zebra mussels, and their
congeners the quagga mussels (
Dreissena rostriformis
bugensis
), are eradicated from the lakes they have
invaded, instead of being used as biofi ltrators (Strayer
2009). Both the zebra mussel and the quagga mussel
have caused much economic and ecological damage by
settling on hard substrates where they clog pipes of the
cooling systems. These mussels strongly compete with
other fi lter feeders and disrupt lake food webs.
Eradi-
cation
programmes in North America will have diffi -
culties in achieving success because these mussels
reproduce readily and fast.
Adjusting w ater l evel fl uctuations
18.3.3
Other measures
Shallow lakes are particularly sensitive to rapid changes
in water level. Therefore, water level fl uctuations (WLF)
may have an overriding effect on shallow lake ecosys-
tem functioning and management (Coops & Hosper
2002). Water levels in shallow lakes naturally fl uctu-
ate both seasonally and annually depending largely on
regional climatic conditions and past and current
human activities (Beklioglu
et al
. 2001). WLF can also
be disastrous for submersed plant communities.
Extremely high water levels in the vegetation period
reduce light availability, and low water levels may
damage plants due to ice and wave action during
There are several other measures available for lake res-
toration. In this section, we will highlight only three
that are science-based, aimed at counteracting acidifi -
cation, excessive water level fl uctuations and oxygen-
poor conditions, respectively.
Restoration of a cidifi ed s ystems
Actions to reduce acidifying emissions in Europe, the
United States and Canada began in the mid-1970s,