Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
burst of a neuron
burst of a different neuron
in HVC
in HVC
neuron
in RA
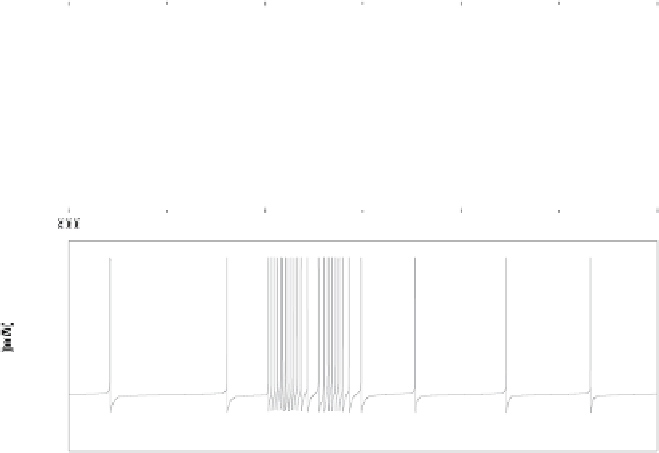
Fig. 8.3.
The voltage of two units emulating neurons in HVC (
a
), and the voltage
of a unit emulating a neuron in RA (
b
). Adapted from [Abarbanel et al. 2004a]
Hodgkin-Huxley (HH) equation
C
M
dV
Hj
dt
=
I
L
+
I
j
Na
+
I
j
K
+
I
j
HE
+
I
j
HI
,
(8.5)
where we have included the leak, sodium and potassium currents in the fash-
ion described in the previous section. In addition, a synaptic current
I
HE
from the previous excitatory unit is considered, as well as a synaptic current
I
HI
from the single inhibitory unit. When isolated, each excitatory HVC neu-
ron is silent and has a resting potential of approximately
−
65 mV. Leak and
ionic currents are constructed, as before:
I
L
=(
E
L
−
V
Hj
)
G
j
L
,
(8.6)
I
j
Na
=(
E
Na
−
V
Hj
)
G
j
Na
,
(8.7)
I
j
K
=(
E
K
−
V
Hj
)
G
j
K
,
(8.8)
where
E
Na
and
E
K
are the equilibrium potentials of the corresponding ionic
currents, and
E
L
is the equilibrium potential for the leakage current.
G
j
L
is
the (constant) conductance for the leak current, and
G
j
Na
and
G
j
K
are the
voltage-dependent, ion-specific channel conductances, which are given by
G
j
Na
(
V
Hj
)=
g
Na
m
j
h
j
,
(8.9)
G
j
K
(
V
Hj
)=
g
K
n
j
,
(8.10)