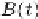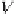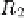Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
A second important configuration of an op-amp, for the purpose of build-
ing our synthesizer, is the one displayed in Fig. 7.2b. The current charging
the capacitor is simply
I
=
V
in
/R
, since no current enters the op-amp. On
the other hand, since
V
−
∼
V
+
=0,
V
in
R
C
dV
out
dt
=
−
.
(7.21)
Therefore,
1
RC
V
out
=
−
V
in
dt ,
(7.22)
allowing us to integrate the input signal. With these elements, we have built
an analog integrator for the simplest model describing labial motion in the
syrinx.
7.2.2 An Electronic Syrinx
In Fig. 7.3, we display an analog integrator for the system of equations under
analysis. Following the circuit clockwise from the top, we see first an arrange-
ment of an op-amp, resistor and capacitor like the one displayed in Fig. 7.2b,
i.e., an integrator. The voltage obtained is
v
=
(1
/RC
)
wdt
. The voltage
V
a
is obtained by multiplying
v
and an external signal
(
t
), which represents
the varying tension of the syringealis ventralis muscle. The operation of mul-
tiplying can be performed by means of an integrated circuit (for example, an
AD633JN multiplier), which multiplies the signals and divides the result by
−
−
+
−
+
−
+
−
+
Fig. 7.3.
An electronic syrinx. This device integrates by an analog method the
equations of a very simple model for the labial motions. When it is connected to a
loudspeaker, a synthetic song is generated