Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
scheme describe above (lower left). If, for instance, 54% of the pyruvate is
unlabeled and 46% carries a
13
C at the first position, it can be inferred that
92% of the glucose was processed via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, and 8%
via the Pentose-phopshate pathway (right side of the figure).
5.1.2 Metabolic Flux Analysis
Flux distributions, that is, the set of reaction rates (= fluxes) of the system
under consideration, are the integrated network responses of the different cell
components (genes, mRNAs, proteins, and metabolites) and abiotic physico-
chemical system parameters. They can be used to decipher cellular functions
and guide rational strain engineering for industrial biotechnology. In contrast
to the quantification of cellular components (mRNA, proteins and metabo-
lites), fluxes are not directly accessible by experimental techniques but have
to be inferred using mathematical models of the cellular metabolism.
Fig. 5.2
Stoichiometry at steady state
Assuming that the system is in a stationary or quasi-stationary state (i.e.,
that metabolite concentrations and reaction rates do not change over time),
reaction rates can be calculated applying metabolic flux analysis, which is
based on metabolite mass balances. Figure 5.2 gives an example: Knowledge
about the stoichiometry of the reaction network (composed of the the inter-
nal fluxes
r
1
, ...
r
6
and extracellular uptake and secretion rates, the exchange
fluxes
b
1
, ...
b
4
) is sucient to set up a linear equation system. In matrix no-
tation this linear equation system reads:
S
∗
v
=0.Thematrix
S
contains the


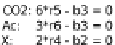



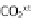































































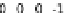














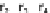
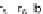

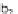

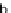





Search WWH ::

Custom Search