Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
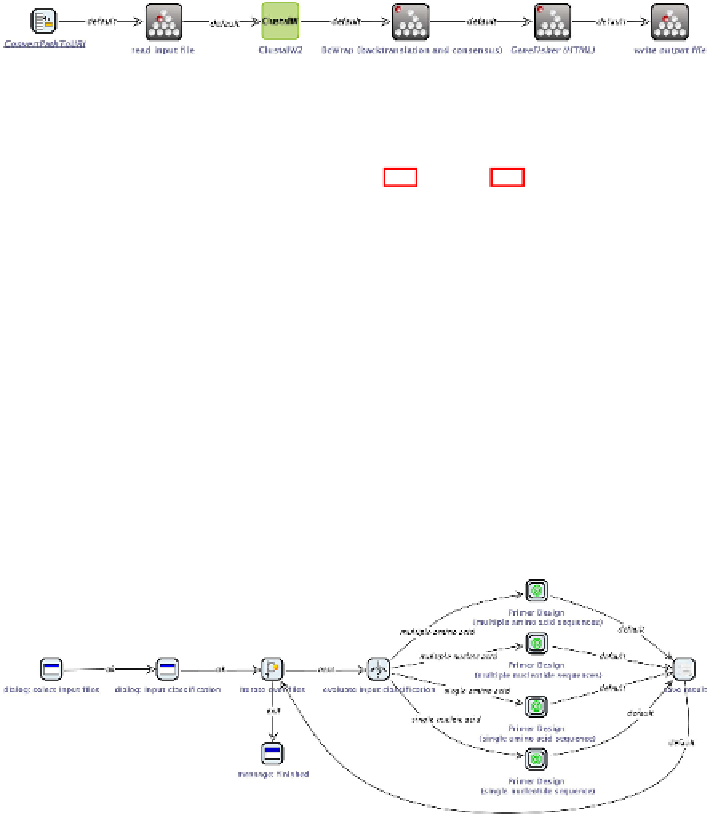
Fig. 4.6
Primer design for multiple amino acid sequences
The subworkflows are tailored to a specific input sequence type, according
to the abstract workflow given in Figure 4.4. Figure 4.6 shows the subwork-
flow for primer design based on multiple amino acid sequences: the given
input file name is transformed into an URI (ensuring that the file is read-
able at each platform), its content is read, and then sequence alignment,
backtranslation and consensus calculation are performed prior to the actual
primer design. Finally, the result is written into a file. The subworkflow for
primer design based on multiple nucleotide sequences is highly similar, only
the backtranslation step is omitted. In case of a single amino acid sequence,
backtranslation is necessary, but the alignment and consensus calculations
steps are not required. Single nucleotide sequences need no preprocessing at
all.
4.2.3 Batch Processing GeneFisher-P Workflow
Fig. 4.7
Batch processing GeneFisher-P workflow
As mentioned before, it is not feasible to design large numbers of primers
when the process has to be carried out interactively (which is the case for the
very interactive GeneFisher web application as well as for the GeneFisher-
P workflow discussed before, where basic information about the data has
to be provided at runtime). The workflow shown in Figure 4.7 reduces the
required interaction to a minimum: only the input files and the types of
the input sequences have to be specified, then the files are worked off by the
corresponding subworkflow within a loop autonomously in a batch processing
manner.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search