Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
HA or NA protein present in the mixture was immunoprecipitated by anti-AIV poly-
clonal serum. After three rounds of washing, the bound P1 was detected by anti-His
monoclonal antibodies (Novagen, USA). The P1 peptide was detected only in the HA
complex (Figure 9). There was no P1 peptide visible in the NA complex (data not
shown). This experiment confirmed the interaction of the P1 peptide to the HA protein.
Figure 9.
Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitated HAt-P1 complex.
In vitro
translated NA
protein or HA
t
protein was mixed with P1 peptide and the complex was co-immunoprecipitated
using anti-AIV serum and the eluted complex was analyzed by SDS-15% PAGE, electrotransferred to
a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with anti-His monoclonal antibody (Novagen, USA). Lane 1:
HA
t
and P1 complex; Lane 2: NA and P1 complex; For control,
in vitro
translated NA or HA
t
mixed
with control peptide SWGEYDM and detected using anti-His antibodies. Lane 3: HA
t
and Control
peptide complex; Lane 4: NA and control peptide complex; Lane 5:
in vitro
translated P1 peptide
(~12 kDa). The arrow indicates the precipitated P1 protein in the HA
t
-P1 complex and the
in vitro
translated P1 peptide.
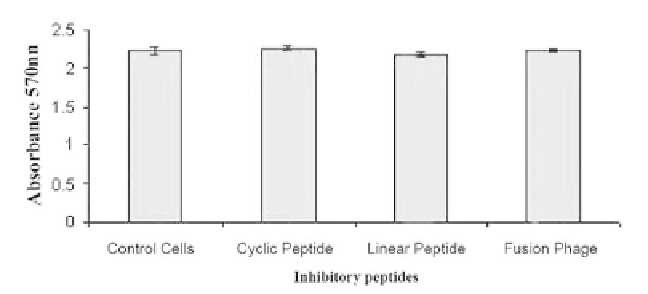
Peptide Toxicity
To analyze the cellular toxicity properties of the peptides and fusion phages, MDCK
cells were exposed to 100 μM of cyclic, linear peptides or 10
13
pfu/100 μl of FP-P1 for
24 hr and the cell viability was determined by MTT assay. There was no significant
difference (Students t test, P > 0.05) observed in the cell viability of control and pep-
tide treated cells (Figure 10).
Figure 10.
In vitro
toxicity of inhibitory peptides. The MDCK cells were treated with 100 μM of C-P1
or L-P1 or 1,014 pfu/ml of FP-P1 and the cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay after 24 hrs of
incubation (mean of three experiments +/- SD). No statistically significant differences in cell viability
were observed (Students t test, P > 0.05).