Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
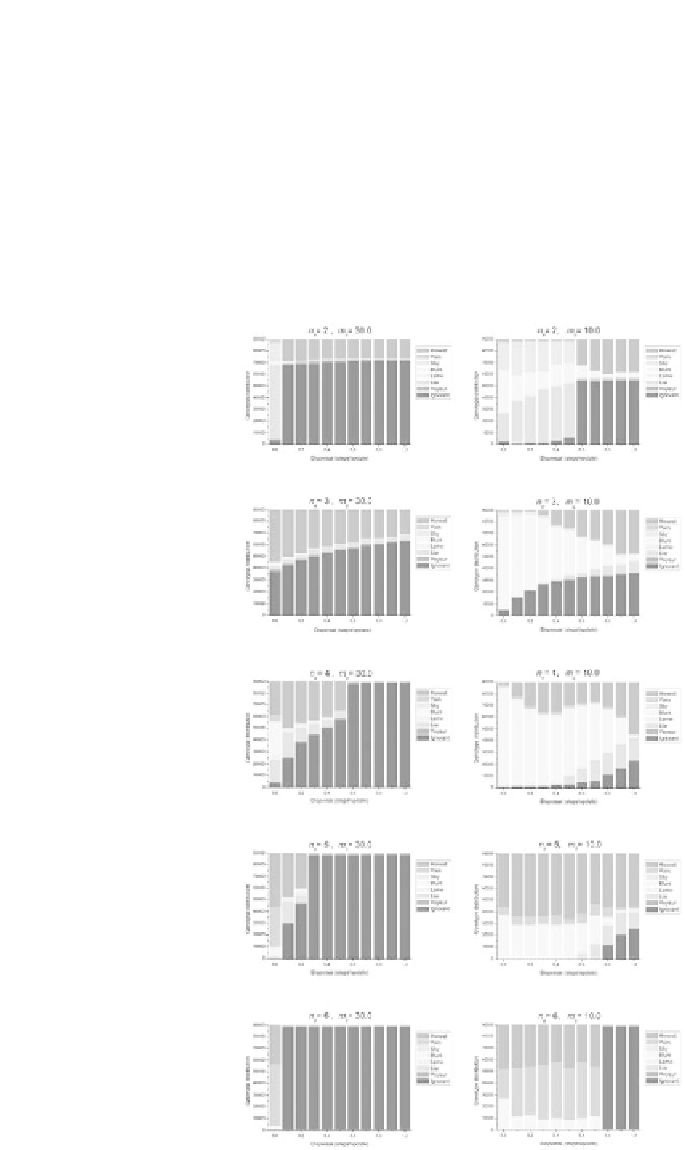
its cost for the cooperators. Therefore both QS alleles (S and R) spread and become
established within the cooperating population. Consequently parasites do not need to
issue fake quorum signals to access the benefi t. Increasing diffusion gradually reduces
the likelihood of maintaining three cooperators in a neighborhood, resulting in a lower
level of cooperation in the population. At very intensive diffusion (D = 6.0 in this pa-
rameter setting) both cooperation and QS disappear together abruptly, and the stage is
left for the parasitic “Ignorant” type. Apparently then successful cooperation will be
so rare that cooperators are losing more due to the cost of operating the QS machinery,
than gaining from the cooperation benefi t. Consequently, their relative fi tness shrinks
below that of the “Ignorant” type, and they vanish.
Figure 3.
Stationary genotype distributions of the QS-disabled set of simulations.
All parameters as
in Figure 1. except μ
s
= μ
r
= 10
−
4
.