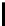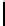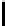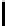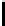Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Reprinted from Sadhana 18
− II
(1993), P. P. Das and B. N. Chatterji,
Digital Distance Geometry: A Survey
,
159-187, Copyright (1993), with permission from Indian Academy of Sciences.
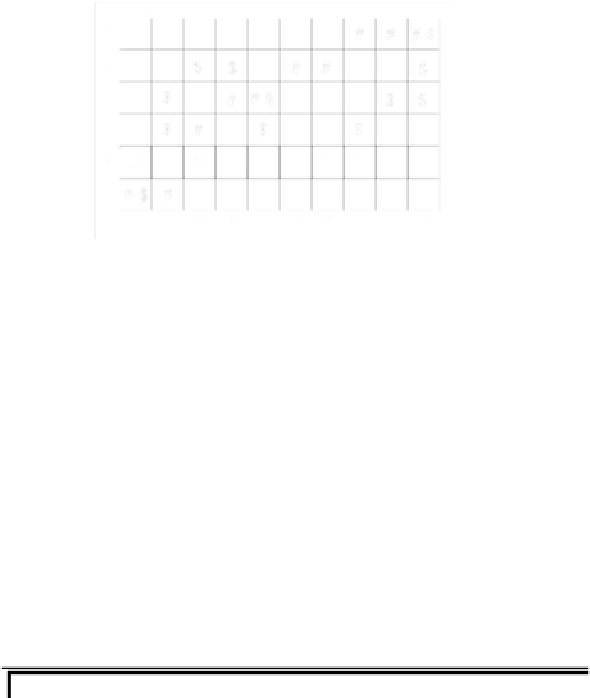
FIGURE 2.7: Two paths from (0,0) to (9,5) using octagonal distance. The
path Π marked with $ has a length |Π|=15 and the path Π
∗
marked with # has
a length |Π
∗
|=10. Along either path, the adjacency relation alternates between
O(1)-neighbor and O(2)-neighbor. Clearly |Π
∗
| has the minimal length.
represented as
B = {b(i) : i = 1,2,··· ,p;b(i) ∈{1,2,··· ,n}}
where p = |B| is called the period or length of the sequence.
€
A few N-Sequences in low dimensions are shown below:
n
B
p
n
B
p
n
B
p
2 {1}
1
3 {1}
1
4 {1}
1
2 {2}
1
3 {2}
1
4 {2}
1
2 {1,2}
2
3 {3}
1
4 {3}
1
2 {2,1}
2
3 {1,2}
2
4 {4}
1
2 {1,2,2}
3
3 {2,3}
2
4 {1,2}
2
2 {1,2,2,2}
4
3 {1,3}
2
4 {2,3}
2
2 {1,2,1,2,2} 5
3 {1,2,3}
3
4 {1,2,4}
3
2 {2,2,1,1,1} 5
3 {2,3,1,2,2,3} 6
4 {1,2,2,3,4} 5
Definition 2.20. Given an N-Sequence B, the notion of an N(B)-path
Π(u,v;B) between u,v ∈ Z
n
extends naturally from the definitions of digital
paths (Section 2.2.2) using neighborhood set N(B). On such a path, neighbor-
hood relations are cyclically used from the N-Sequence B.
The minimal path is denoted by Π
∗
(u,v;B).
€
Definition 2.21. The Sum Sequence F = {f(1),f(2),··· ,f(p)} of an N-
Sequence B = {b(1),b(2),··· ,b(p)} is defined as
i
j=1
b(j) ∀i,1 ≤ i≤ p.
f(i) =