Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
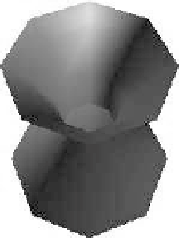
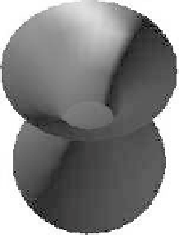
(a) k = 4
(b) k = 7
(c) k = 20
FIGURE 7.11: Results on quad-decomposition for a digital jug: Approxi-
mating generating digital circles by regular 2k-gons. (See color insert.)
Reprinted from
International Journal of Arts and Technology
,
4
: 196-215, G. Kumar et al., Copyright 2011, with
permission from Inderscience Publishers.
differing by at most unity. If their distances from α are the same, then it is easy
to observe that the surface C
Z
i
∪C
Z
i+1
is digitally connected and irreducible.
The problem arises when p
i
and p
i+1
have their respective distances from α
differing by unity. Then there may arise some missing voxels trapped between
C
Z
i
and C
Z
i+1
, which results in digital disconnectedness in the surface C
Z
i
∪
C
Z
i+1
, as shown in Fig. 7.10. Detection of these missing voxels is performed
to achieve a digitally connected surface, namely S
G
:= C
Z
1
∪C
Z
2
∪...∪C
Z
n
,
as follows.
Case 1 (r
i+1
> r
i
): While generating the digital circle C
Z
i+1
parallel to
the zx-plane corresponding to the point p
i+1
∈ G, there is either an east
(E) transition or southeast (SE) transition from the current point q(x,y,z)
in Octant 1 (z 6 x 6 r
i+1
) [84]. If we take the respective projections, C
Z
′
i
and C
Z
′
i+1
, of C
Z
i
and C
Z
i+1
on the zx-plane, then C
Z
′
i
and C
Z
′
i+1
become
concentric with their radii differing by unity. As r
i+1
> r
i
, each run-length
λ
(k)
i+1
(k > 0) of C
Z
′
i+1
in Octant 1 is either the same as the corresponding run-
length λ
(k
i
of C
Z
′
i
or greater by unity [14]. Hence, a missing voxel between C
Z
i
and C
Z
i+1
is formed, only if there is a transition toward SE (a change in run,
thereof) from a point/pixel in C
Z
′
i+1
giving rise to a missing pixel between C
Z
′
i
and C
Z
′
i+1
. We detect such missing pixels by determining whether or not there
is a “miss” during each SE transition for C
Z
′
i+1
. More precisely, if the point
next to the current point q(x,z) ∈C
Z
′
i+1
in Octant 1 is (x−1,z + 1) and the
′
i
, then we include the point (x−1,y,z)
in C
Z
i+1
between (x,y,z) ∈C
Z
i+1
(x−1,y,z + 1) ∈C
Z
i+1
.
Case 2 (r
i+1
< r
i
): If the point next to the current point q(x,z) ∈C
Z
′
point (x−1,z) does not belong to C
Z
i+1
in Octant 1 is (x− 1,z + 1) and the point (x,z + 1) does not belong to C
Z
′
i
,