Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
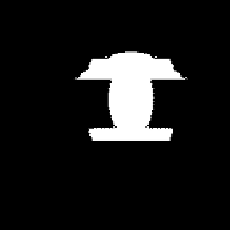
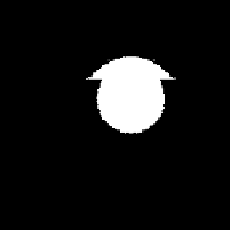
FIGURE 6.23: Cross-sections obtained by intersecting a plane passing
through the center and with a normal along the direction (−1,1,−1) with
the objects using MAT representation from {3}: (a) DUMBCONE, (b) DUM-
BLE, and (c) SPHCONE.
Reprinted from
Pattern Recognition Letters
, 21(2000), J. Mukherjee et al., Fast Computation of Cross-Sections of
3-D Objects from Their Medial Axis Transforms, 605-613, Copyright (2000), with permission from Elsevier.
domain. Hence, the points, which are missed in the cross-sections computed
from voxel representation, are covered by the algorithm CSUM. This feature
improves the quality of the results (see Figs. 6.23).
The time complexity of the voxel-based algorithm for computing the cross-
sections of the 3-D voxel data of size n×n×n is O(n
3
). But the algorithm
CSUM takes linear time in the number of medial spheres. As the number
of medial spheres in the MAT is much less than the number of voxel data,
the computation time is su
ciently reduced. In this case also, it is advisable
to use the distance function, which usually provides less number of medial
spheres. In [152], it was shown experimentally that the octagonal distance
{3} yields the fewest medial spheres in most cases in the family of octagonal
distances. It has this feature, because the volume of a medial sphere (in the
form of a cube) is the largest in the family. It has also the least number of
edges (12 in number), thus saving time in the computation of intersecting
points with edges of medial spheres. Considering the above two properties,
it is recommended to use {3} as the distance function for deriving MATs of
objects to compute cross-sections. To demonstrate the varying numbers of
medial spheres for different distance functions, a few typical examples (from
[152]) are shown in Table 6.4. We observe that{3}does not necessarily provide
the least number of medial spheres in all objects. The number also depends
on the shape of the object. The other interesting fact, we should note here, is
that the quality of the result does not depend on the choice of an octagonal
distance. In this case, the results are almost the same with those obtained
from voxel representation after the inclusion of missing or unmapped points
[152].