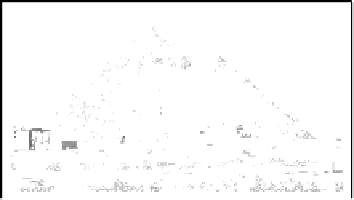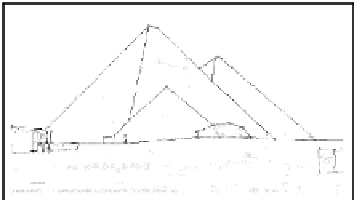Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
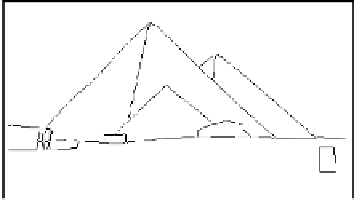
FIGURE 4.1: Polygonal approximation of the image '
pyramid
'. Top-left: 8-
bit gray-scale image of '
pyramid
'. Top-right: The edge map of '
pyramid
' is
considered to be a real-world digital curve. Note that the edge map is sub-
ject to the parameter(s) specified in the edge extraction algorithm. Bottom-
left: Polygonal approximation of the edge map with the vertices shown in red
color and the edges in blue color. Bottom-right: Polygonal approximation
superimposed on the original gray-scale image shows how well the algorithm
can approximate a real-world image. (See color insert.)
1990s [50, 73, 74, 122, 142, 195]. In the previous chapter, characterization of
digital straightness property of a set of points in a 2-D grid by determining the
domain of a candidate DSLS was briefly discussed. In this chapter, we present
a more direct approach for determination of the straightness of a digital arc
and demonstrate its application in polygonal approximation of boundaries of
objects in an image.
A typical example of this application is shown in Fig. 4.1. It depicts a
polygonal approximation of a real-world digital curve defining the edge map
of the '
pyramid
' image.
1
The merits of this approach lie in its superior per-
formance on computational speed and quality of results compared to other
methods of polygonization of edge points. The polygonal approximation is
achieved (refer to Fig. 4.1) only in a few milliseconds from the digital curve,
since it uses only a few primitive operations in the integer domain only. This
shows the potential strength of a digital-geometric technique compared to the
others, which are mostly based on parametric approaches, such as distance
criteria, usage of masks, eigenvalue analysis, Hough transform, etc.
1
Source: The Berkeley Segmentation Dataset and Benchmark,
http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/Projects/CS/vision/bsds/
.