Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
primer was introduced to chitosan by the reductive amination using
NaBH
CN in a mixed solvent of aqueous acetic acid/methanol to give a
maltooligosaccharide-grafted chitosan. This material was converted
into a maltooligosaccharide-grafted chitin by
3
-acetylation using
acetic anhydride. Then, the phosphorylase-catalyzed enzymatic
polymerization of Glc-1-P from the maltooligosaccharide primers on
these chitin and chitosan derivatives was performed to obtain the
amylose-grafted chitin and chitosan.
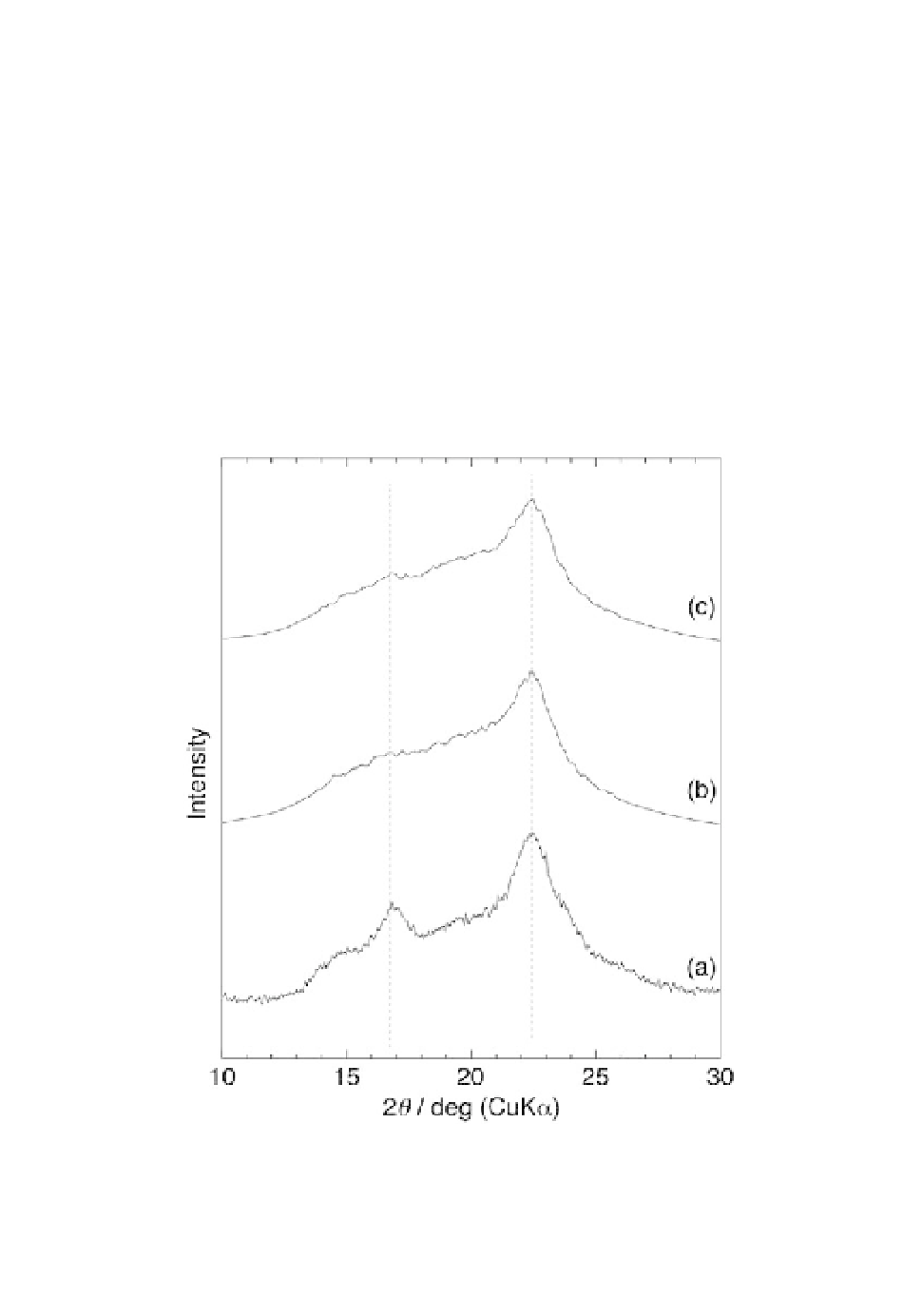
The amylose-grafted chitin and chitosan were insoluble in any
solvents, e.g., aqueous acetic acid and DMSO, which were good
solvents for chitosan and amylose, respectively. The XRD patterns of
these materials showed typical
N
-type crystalline structures owing
to amyloses (Fig. 6.2). Such crystalline structures are generally
A
Figure 6.2
XRD patterns of amylose (a), amylose-grafted chitosan (b), and
amylose-grafted chitin (c).