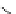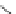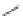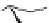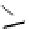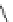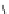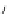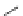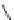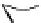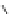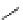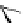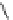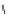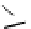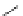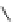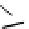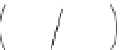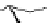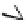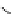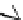Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
O Si
O Si
O Si
O Si
OAc
O
n
AcO
AcO
OAc
n
OAc
O
HN
NH
2
OAc
+
O
AcO
AcO
O
O
OAc
AcO
AcO
OAc
O
5
OAc
OAc
O
OAc
OAc
O
AcO
O
OAc
OAc
5
O
AcO
O
OAc
Deacetylation
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
O Si
O Si
O Si
O Si
OH
OH
O
O
HO
HO
HO
HO
OH
n
Glc-1-P
Phosphorylase
OH
n
OH
O
OH
O
HN
HN
O
O
HO
HO
HO
HO
OH
O
OH
O
O
O
5
m
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
(b)
OAc
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
C
H
3
CH
3
C
H
3
O
O Si
O Si
AcO
AcO
O Si
O Si
OAc
Hydrosilation
H
n
OAc
O
n
OAc
OAc
+
O
AcO
O
OAc
O
O
AcO
AcO
OAc
5
O
AcO
OAc
OAc
O
OAc
O
AcO
OAc
O
O
5
O
Deacetylation
AcO
OAc
OH
OH
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
O
O
HO
HO
O Si
O Si
HO
HO
O Si
O Si
OH
OH
Glc-1-P
Phosphorylase
O
OH
O
OH
n
n
OH
OH
O
O
HO
HO
O
O
O
O
OH
OH
O
5
O
5
HO
HO
OH
OH
Figure 5.7
Chemoenzymatic
synthesis
of
amylose-grafted
polydimethylsiloxanes using Glc
lactone derivative (a) and
7
allylated Glc
(b) by means of phosphorylase-catalyzed
enzymatic polymerization.
7
[36]. Therefore, saccharide-PDMS hybrids would be expected to
have a significant potential for biological applications.
Therefore, amylose-grafted PDMSs were synthesized as
follows [37,38]. First, maltooligosaccharide-grafted PDMSs were
prepared by the reaction of a Glc
lactone derivative with an amine-
functionalized PDMS (Fig. 5.7a) or the hydrosilylation of an allylated
Glc
7
with a PDMS derivative having Si-H linkage (Fig. 5.7b), followed
by deacetylation. Then, the phosphorylase-catalyzed polymerization
of Glc-1-P using the maltooligosaccharide-grafted PDMSs was
carried out to give the amylose-grafted PDMSs. These are indicated
as the synthetic route (i)
7
→
(iii)
→
(vi) in Fig. 5.1.