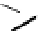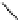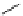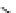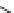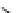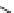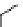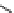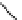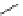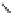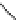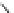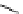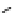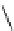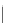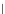Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
attention in terms of application as a polarizing material for liquid
crystal displays (LCDs). The polarized film in LCD is generally
prepared based on the PVA/iodine complex [29,30]. However,
because iodine is easily released from the PVA backbone under
relatively high temperature and/or high humidity conditions, this
film is susceptible to heat and moisture. Therefore, the PVA-based
polarized film is practically used by being sandwiched between
protecting films such as triacetylcellulose (TAC) films. Development
of a sole film, which has an ability to stably retain iodine without the
use of the protecting film, is hopefully expected.
Amylose is a well-known host compound that forms a stable
inclusion complex with iodine [31]. Therefore, a blend film composed
of PVA and amylose is possibly one of the candidates for such a new
polarized film stably retaining iodine without the use of TAC [32,33].
However, the blend film may have heterogeneous distribution of
amylose chains in PVA matrix due to their aggregation. To obtain such
a film stably retaining iodine, a PVA derivative covalently bonded to
amylose, e.g., an amylose-grafted PVA, was prepared.
An amylose-grafted PVA was synthesized by the chemoenzymatic
method (Fig. 5.5) [34]. First, Glc
was introduced to an amine-
functionalized PVA by the reductive amination using NaBH
7
CN
3
OH
O
OH
n
+
OH
O
O
NH
O
HO
HO
OH
OH
O
O
OH
HO
OH
O
OH
5
HO
NaBH
3
CN
H
2
N
Glc-1-P
Phosphorylase
n
n
OH
O
O
NH
OH
O
O
NH
OH
OH
O
O
OH
OH
O
O
HO
HO
HN
HO
HO
HN
OH
OH
O
HO
O
HO
OH
HO
HO
OH
5
O
m
O
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
Figure 5.5
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of amylose-grafted poly(vinyl
alcohol) by means of phosphorylase-catalyzed enzymatic
polymerization.