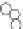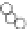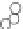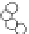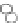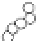Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
reaction of polysaccharides with polymeric main chains is quite
difficult.
Therefore, by means of the combination of the enzymatic
polymerization forming amylose, as described in Chapter 4, with a
chemical reaction, i.e., a chemoenzymatic approach, several research
groups have developed amylose-grafted polymeric materials
with well-defined structures (Fig. 5.1) [6,7]. “Macromonomer
method” and “polymer reaction method” are generally known as
the preparation methods for the amylose-grafted polymers. One
of the synthetic routes for the macromonomer methods is that the
maltooligosaccharide primer first reacts with the polymerizable
compound (monomer) to obtain the maltooligosaccharide-containing
monomer (macromonomer) (ii), polymerization of the resulting
macromonomer or copolymerization of this macromonomer with
(i) Polymerization
Monomer
Polymer backbone
(ii) Chemical reaction
(iii) Chemical reaction
Maltooligosaccharide
Maltooligosaccharide
(iv) Polymerization
Monomer
Maltooligosaccharide-
containing monomer
Maltooligosaccharide-grafted polymer
(v) Phosphorylase-catalyzed
enzymatic polymerization
(vi) Phosphorylase-catalyzed
enzymatic polymerization
Glc-1-P
Glc-1-P
Amylose-chain
(vii) Polymerization
Monomer
Amylose-containing
monomer
Amylose-grafted polymer
Figure 5.1
Schematic reaction for chemoenzymatic synthesis of amylose-
grafted
polymers
by
means
of
phosphorylase-catalyzed
enzymatic polymerization.