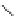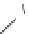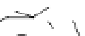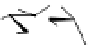Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
HO
O
HO
HO
O
O
HO
+
HO
OH
HO
HO
O
HO
OH
O
HO
OH
O
O
P
O
OH
O
HO
OH
O
n
Glc-1-P
Maltooligosaccharide
(Primer)
Phosphorylase
HO
O
HO
O
HO
OH
+
Inorganic phosphate
HO
HO
HO
OH
O
O
OH
HO
OH
O
n+1
Amylose
Figure 4.1
Phosphorylase-catalyzed
enzymatic
polymerization
to
amylose.
molecular weight of the produced amylose has a narrow distribution
(
< 1.2) and can be controlled by the Glc-1-P/primer feed
molar ratios [4].
It has been reported that phosphorylase from rabbit muscle
is more suitable for the synthesis of amylose with low molecular
weight in DPs ranging 10-20 than that from potato [3].
M
/
M
w
n
4.2
Thermostable Phosphorylase Catalysis
The phosphorylase from potato has been studied extensively and is
known to elongate the
α
-glucan chain rapidly by using maltotetraose
as a primer. However, the potato phosphorylase is not suitable for
industrial processes because of its low thermostability. Amylose is
known to precipitate at low temperatures, but this can be significantly
inhibited at elevated temperatures. Thermostable phosphorylases
have been employed for the enzymatic synthesis of amylose at
elevated temperatures. The phosphorylase genes from several
thermophilic microorganisms such as
Bacillus stearothermophilus
[4],
Thermus thermophilus
[5],
Thermococcus litoralis
[6], and
Thermus aquaticus
[7] have been isolated.
showed extensive thermal
stability where the enzyme retained 80% of its activity even after
Phosphorylase from
T. aquaticus