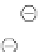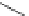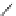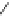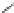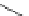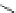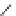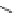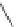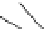Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
OH
HO
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
HO
HO
HO
OH
+
O
OH
OH
OH
HO
HO
O
HO
O
P
O
O
HO
2
O
Man-1-P
Glc
4
phosphorylase
H
O
O
O
HO
O
HO
HO
+ inorganic phosphate
OH
OH
OH
HO
HO
O
HO
O
HO
3
α
-
D
-mannosyl-(1
�
4)-Glc
4
α
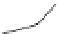
Figure 3.11
Phosphorylase-catalyzed
-mannosylation of Glc
using Man-
4
1-P.
-glucose
1-phosphate (dGlc-1-P) in a two-step process (Fig. 3.12) [35]. First,
a 2-deoxyglucose unit is transferred to the
Withers
et
al
.
enzymatically
prepared
2-deoxy-
α
-glucan primer that is
catalyzed by inorganic phosphate. In the second step, 2-deoxyglucose
is released by phosphorolysis to produce dGlc-1-P and in the overall
reaction the primer remains unchanged. On the basis of this study,
1,2-dideoxyglucose (glucal) was applied as a glycosyl donor in
considerable excess in order to shift the equilibrium to the chain
elongation with a glucal to primer ratio of 15:1 for the occurrence
of 2-deoxyglucosylation in the presence of inorganic phosphate
(Fig. 3.13) [36]. After the phosphorylase-catalyzed reaction in the
presence of glucal, Glc
α
, and only 0.05 equiv. of phosphate for 6 h,
4
2-deoxy-
-glucosylated penta-, hexa-, and heptasaccharides were
separated by size exclusion chromatography in 17%, 12%, and
8% yields, respectively. Additionally, a fraction of higher molecular
weight with an average DP of 12 was obtained in 33% yield.
Withers also reported the phosphorylase-catalyzed glycosylation
of glycogen with 3- or 4-deoxy-
α
-glucose 1-phosphates. However,
only averages of up to 1.5 units were transferred [37].
Oligosaccharides containing GlcN units and its derivatives, e.g.,
GlcNAc, serve key functions for living organisms such as in cell-cell
recognition and immune responses. The preparation of saccharide
chains containing GlcN residues, therefore, has been frequently
required for the various studies in glycoscience. Much effort has
α