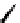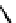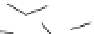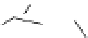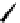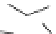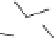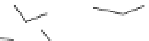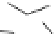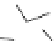Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
OH
OH
NHAc
O
NHAc
O
O
HO
HO
chitinase
O
HO
O
HO
HO
O
O
NHAc
O
OH
OH
N
n
chitin
CH
3
(b)
OH
OH
OOC
O
OOC
O
O
HO
hyaluronidase
O
HO
HO
O
O
HO
O
HO
O
OH
NHAc
N
OH
n
hyaluronan
CH
3
(c)
HO
OH
HO
OH
OOC
O
OOC
O
O
hyaluronidase
O
HO
O
O
HO
O
HO
OH
O
NHAc
OH
N
n
chondroitin
CH
3
Figure 2.5
Hydrolase-catalyzed polymerization of sugar oxazolines to
synthetic chitin (a), hyaluronan (b), and chondroitin (c).
2.3
Synthesis of Polysaccharides Catalyzed by
Sucrase-Type Enzymes
Non-Leloir-type glycosyltransferases that use sucrose as a substrate
are able to catalyze the synthesis of polysaccharides in high yields
under kinetic control, even in dilute aqueous solution of sucrose
[9]. Most enzymes of this class highly specialize in transfer of
either the glucose or the fructose moiety of sucrose, giving glucose-
based polysaccharides (glucans) or fructose-based polysaccharides
(fructans) of different types with respect to glycosidic linkages and
side chains. The simplified reaction schemes are shown as follows:
Glucosyltransferases
n
sucrose
glucan +
n
fructose
Fluctosyltransferases
glucose
The enzymes of this group are often called sucrase-type
enzymes, i.e., glucosyltransferases are glucansucrases and fructosyl-
transferases are fructansucrases.
Glucansucrases are typically extracellular enzymes, which are
produced mainly by lactic acid bacteria [30]. Dextran-, mutan-,
n
sucrose
fructan +
n