Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
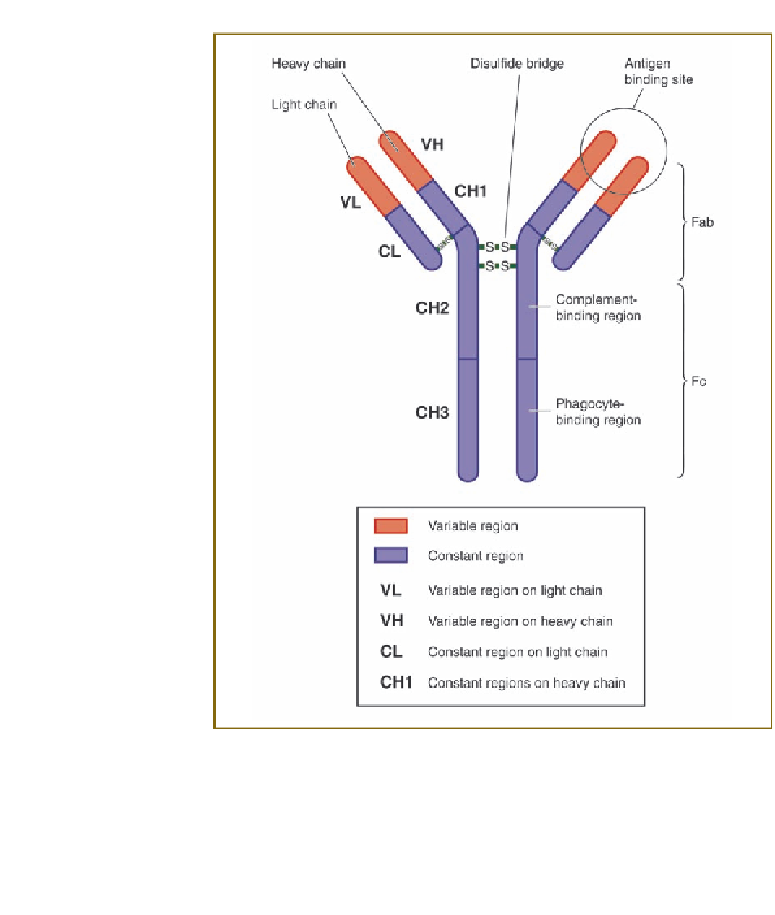
Figure 4.5
The most common antibody molecule is a complex combination
of two identical light and two identical heavy chains, held together by
weak bonds formed by sulfur-containing amino acids. The four variable
regions form the antigen binding site; the constant regions allow the
antibodies to trigger the cell-damaging complement cascade and signal
phagocytic cells to engulf and break down invading microbes.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search