Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
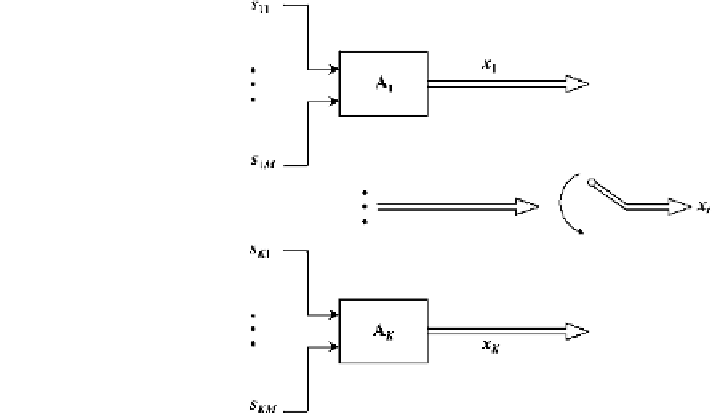
Fig. 2.3 Outline of the ICA
mixture model
The Extended InfoMax algorithm [
23
] is used for adapting the basis functions
(mixture matrix) in the ICA model. The gradient ascent technique is used to
maximize the log-likelihood function. The rules to update the basis functions A
k
and the bias vectors b
k
for every class are the following
Þ
A
k
I
K tanh s
ðÞ
s
k
s
k
s
k
DA
k
/
pC
k
j
x
t
;
H
ð
ð
2
:
37
Þ
b
k
¼
P
t
¼
1
x
t
pC
k
j
x
t
;
H
ð
Þ
P
k
¼
1
pC
k
j
x
t
;
H
ð
2
:
38
Þ
ð
Þ
For the automatic switching between super-gaussian and sub-gaussian source
distributions, a switching matrix O
k
;
l
is used. Super-Gaussian
: log p s
ðÞ
O
k
;
l
¼
1
: log p s
ðÞ/
P
log cosh s
k
;
l
/
P
n
n
j
s
k
;
l
j;
and Sub-Gaussian
O
k
;
l
¼
1
l
¼
1
l
¼
1
s
k
;
2
Þ:
where n is the dimensions of the source, s
k
;
l
is the lth dimension of the
source
in
the
kth
class,
and
O
k
;
l
is
an
index
which
allows
for
automatic
switching
between
super-gaussian
and
sub-gaussian
models
[
23
]
O
k
;
l
¼
h i
.
The algorithm was tested to automatically identify different contexts in BSS
(each context featured by the parameters of an ICA model), assuming the number
of classes K to be known. An extension was made in [
61
] where the number of
clusters and the intrinsic dimension of each cluster were determined by a varia-
tional Bayesian method similar to the method proposed in [
59
]. Recently, an on-
line version for partitioning the input-output space for fuzzy neural networks was
proposed in [
62
]. In this algorithm, one cluster is generated for the first data vector.
For new data, a decision is made to generate or not generate new clusters
Es
k
;
no
E
s
k
;
l
tanh s
k
;
l
s
k
;
l
sign E sech
2
Search WWH ::

Custom Search