Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3
1
+ Global
1
0
4
-1
+ Deductive
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
-2
Understanding
-3
Organization
-4
2
-5
+ Sequential
+ Inductive
-6
4
5
6
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
Processing
+ Active
+ Reflective
Fig. 7.8
Three sources in a learning style space for graduate courses with grades
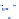
Fig. 7.9 Measures of
clustering validation with
three sources
1.6
1.4
partition entropy coefficient
partition coefficient
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
number of clusters
Figure
7.10
shows three sources for graduate courses with no grades. The
distribution of the data in Fig.
7.10
does not allow learning style groups to be
formed and shows all the subjects within a single learning style. Since the
understanding and organization dimensions do not discriminate the projection of
the learning styles, only the processing dimension provides some discrimination.
Therefore, a single learning style that emphasizes reflection over practice is
obtained. This is apparent in the content consulting and exercise practice com-
ponents of the processing dimension. The conclusion is that the lack of assessment
does not allow student learning styles to be developed.
The results for regular academic courses were similar to the graduate course
results finding meaningful learning styles for courses with grades. Non-parametric
ICA provided better results than standard ICA algorithms allowing more suitable
learning
styles
clusters
to
be
detected.
Classical
ICA
algorithms
rely
on















































































































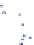





































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search