Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
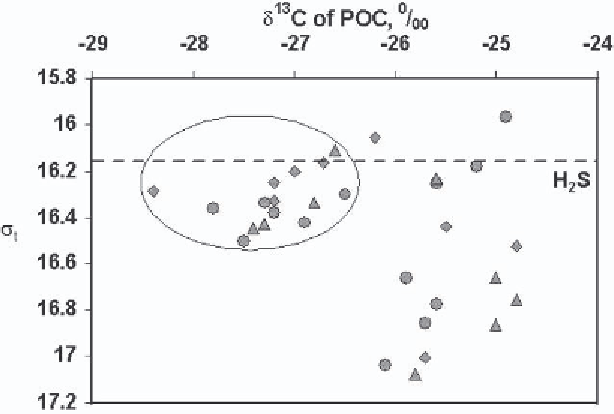
Figure 3.
13
C) of particulate organic carbon (POC) vs.
relative density σ
t
in the open Black Sea. Filled circles are data from Station 5 (43˚14.92'N,
34˚00.11'E, depth 2172 m), filled triangles are data from Station 6 (43˚00.20'N, 34˚30.25'E
depth 2123 m), and filled diamonds are data from Station 4 (44˚20.23'N, 32˚09.54'E depth 1998
m) (modified from [14]).
The carbon isotopic composition (δ
at the same localities. Both, in the Cariaco Basin and in the Black Sea, lateral
transport processes may be largely responsible for this discrepancy, but quanti-
tatively their role in supplying allochtonous CO
2
available for chemosynthesis
was not so far studied and should be addressed by future studies.
5.
COMPOSITION AND ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT
BACTERIOPLANKTON GROUPS IN THE
REDOX-ZONE
Bacteria of the Oxidative Part of the Sulfur Cycle.
Bacteria of the
oxic/anoxic interface usually consist of large rod-shaped
Achromatium
type
bacteria with densities of 100-300 cells ml
−
1
and filamentous (chain-forming)
bacteria are related probably to thiobacilli. The latter represent over 60% of
the total bacterioplankton in the redox zone and their numbers can reach (1-
5)
10
5
cells ml
−
1
[52, 53]. In the Black Sea chemocline Zubkov et al. [64]
observed high cell densities (more than 10
3
cells ml
−
1
) of large strongly motile,
spherical bacteria of 5-20 µm in diameter, which resembled gradient-type, col-
orless, sulfur bacteria of the genus
Thiovulum
. This was the first report on
the presence of these 'sediment' bacteria in pelagic waters. Ten heterotrophic
strains related to the
Rhizobiaceae
family were isolated from the Black Sea
chemocline and were able to oxidize sulfide, elemental sulfur and thiosulfate
×