Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
NaCl
Solution
Water
Diameter
of tube
Length of tube
Outow
1.00
Dispersion
0.50
Piston flow
0.00
0
1
Pore Volume
2
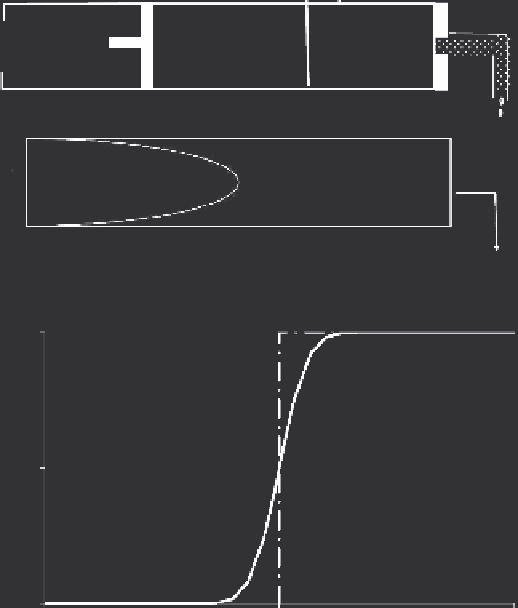
FIGURE 3.5
Piston flow, flow in a narrow tube or a soil pore, and the relative concentration versus pore
volume of the effluent solution.
The effect of dispersion is that of solute spreading, which is a tendency
opposite to that of the so-called piston flow. The schematics of Figure 3.5
provide a comparison of effluent concentration for piston-type flow, which
is characterized by a sharp drop in concentration, that is, no solute spread-
ing, and solute transport in a narrow tube or a soil pore. In the schematic,
the increase in solute spreading is clearly manifested by the advance of the
solute front over time. The change of concentration in the outflow or efflu-
ent solution versus the volume displaced clearly illustrates the difference
between piston flow and that in narrow tubes or soil pores. In the schematic,
the concentration is plotted versus relative volume of accumulated effluent
V/ V
o
,
where
V
o
(cm
3
) is the total pore water volume in the soil pore (or the
piston column) and
V
the accumulated volume of effluent (cm
3
).
When dispersion is neglected, the solute moves at the same velocity and a
solute front arrives as one discontinuous jump. This behavior is called
piston
Search WWH ::

Custom Search