Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
500
Zinc Desorption
Windsor Soil
400
300
200
C
o
= 60 mg/L
C
o
= 80 mg/L
C
o
= 100 mg/L
100
0
50
100
150
200
250 00
350 00
1600
Zn Desorption
Webster Soil
1400
1200
1000
800
C
o
= 80 mg/L
C
o
= 100 mg/L
C
o
= 150 mg/L
600
400
0
200
400
600
800
Reaction Time (h)
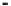
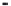
FIGURE 2.12
Zn concentration in Windsor and Webster soils versus time during desorption for various
initial Zn concentrations (C
o
).
To illustrate solute retention behavior (adsorption-desorption) when
first-order or nonlinear kinetic (Freundlich) sorption is considered, several
simulations are presented in Figures 2.14 and 2.15 (Selim, Davidson, and
Mansell, 1976). As shown in Figure 2.14 (top), the linear kinetic adsorption
isotherms are strongly time dependent and even after more than 50 hours
only 90% of equilibrium was achieved. The slow attainment of equilibrium
can be attributed primarily to the magnitude of the reaction rate coefficients
k
f
and
k
b
. Figure 2.14 (bottom) also shows simulated adsorption curves for 10
















































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search