Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
0.6
Windsor soil
Single Zn pulse - Column 1
0.4
Mixed Zn pulse - Column 2
0.2
0.0
0
10
20
30
40
50
Pore Volume (V/V
o
)
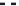
FIGURE 7.27
Breakthrough curves for Zn from a single pulse (column 1) and a mixed (P + Zn) pulse (column
2) in Windsor soil.
of attenuating arsenic bioavailability and toxicity in natural environments
(Smedley and Kinniburgh, 2002). Phosphate (P) anion has similar chemical
properties to arsenate [As(V)] and forms similar types of inner-sphere surface
complex with metal oxides. The competition between As(V) and P for adsorp-
tion sites has the potential of increasing arsenic mobility and bioavailability
in soil environments (Woolson, Axley, and Kearney, 1973; Peryea, 1991).
The competitive adsorption of As(V) and P can be affected by a wide range
of factors, such as surface properties of the adsorbent, concentration and
molar ratio of As(V) to P, solution pH, and residence time (Hingston, Posner,
and Quirk, 1971; Violante and Pigna, 2002; Liu, De Cristofaro, and Violante,
2001; Jain and Loeppert, 2000; Manning and Goldberg, 1996a, 1996b; Zhao
and Stanforth, 2001). Hingston, Posner, and Quirk (1971) proposed two types
of adsorption sites on mineral surfaces. The first type is available for both
As(V) and P where competition takes place while the second type is spe-
cifically available for either As(V) or P. Results from studies on single ion
sorption showed that As(V) and P sorption on Fe and Al oxides were some-
what similar (Manning and Goldberg, 1996a, 1996b). However, when added
simultaneously in equal molarities, Violante and Pigna (2002) reported that
metal oxides and phyllosilicates rich in Fe were more effective in adsorbing
As(V) than P, while more P was adsorbed than As(V) on minerals rich in Al.
Adsorption studies on soils often reveal that P is preferentially adsorbed
than As(V) whether added separately or added simultaneously in equal
molar ratios (Roy, Hassett, and Griffin, 1986a, 1986b; Smith, Naidu, and
Alston, 2002; De Brouwere, Smolders, and Merckx, 2004). These studies also
demonstrated that amounts of As(V) sorbed on minerals and soils exhibited
a decrease with increasing additions of P in solution. Moreover, the sequence






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search