Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
500
Windsor (P = 0 mg/L)
400
300
200
C
o
= 60 mg/L
C
o
= 80 mg/L
C
o
= 100 mg/L
100
0
50 00
150 00
250 00
350 00
600
Windsor (P = 100 mg/L)
500
400
300
C
o
= 60 mg/L
C
o
= 80 mg/L
C
o
= 100 mg/L
200
100
0
50 00
150 00
250 00
350 00
Reaction Time (h)
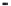
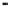
FIGURE 7.21
Zn concentration in Windsor soil versus time during adsorption and desorption for various
initial Zn concentrations. Dashed curves are multireaction model (MRM) simulations.
Figures 7.21 and 7.22 present the amount of Zn sorbed versus time to illustrate
the kinetics of Zn desorption for the various initial concentrations (
C
o
) used.
As illustrated in the figures, Zn desorption exhibited strong time-dependent
behavior as depicted by the continued decrease of the amount sorbed with
time. For Windsor and Olivier soils, the rate of Zn desorption was initially
rapid and followed by gradual or slow reactions. In contrast, for Webster slow
release reactions for Zn were dominant. The results indicate that a fraction of
Zn was weakly sorbed by Windsor and Olivier soils via ion exchange or outer-
sphere surface complexation. In contrast, Zn was strongly sorbed in Webster
soil and bound via inner-sphere surface complexation. Consistent with these


















































































































































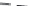

































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search