Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
1.0
0.8
Ca
Mg
0.6
0.4
Na
0.2
0.0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
V/V
o
FIGURE 7.5
Breakthrough results for ternary system (Na, Ca and Mg) in a Sharkey clay soil. Predictions are
based on ion exchange selectivity coefficients for bentonite clay.
broaden the database of land management decisions for agricultural pro-
duction or waste disposal to include such predictions. The applicability of
selectivity parameters of a common type of mineral for prediction of cat-
ion motilities of soils having mineralogies dominated by similar minerals
showed success (see Gaston and Selim, 1990b, 1991). For example, trans-
port model predictions based on selectivity coefficients of pure montmo-
rillonite shown in Figure 7.2 well described cation leaching in columns of
bulk samples of predominantly montmorillonitic Sharkey soil as shown in
Figure 7.5. As reported by Gaston and Selim (1991) good cation predictions
were obtained for a predominantly kaolinitic Mahan soil when selectivity
coefficients were based on pure kaolinite.
Several studies indicated that the affinity of heavy metals to soil matrix
surfaces increases with decreasing heavy metal fraction on exchanger sur-
faces (Abd-Elfattah and Wada, 1981; Harmsen, 1977; Selim et al., 1992; Hinz
and Selim, 1994). Using an empirical selectivity coefficient, it was shown that
Zn affinity increased up to two orders of magnitude for low Zn surface cov-
erage in a Ca background solution (Abd-Elfattah and Wada, 1981). Mansell
et al. (1988) successfully relaxed the assumption of constant affinities and
allowed the selectivity coefficients to vary with the amount adsorbed on
the exchange surfaces. The Rothmund-Kornfeld selectivity coefficient incor-
porates variable selectivity based on the amount of adsorbed or exchanger
composition. The approach is empirical and provides a simple equation that
incorporates the characteristic shape of binary exchange isotherms as a func-
tion of equivalent fraction of the amount sorbed as well as the total solution




























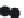


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search