Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Domain Ontology
Sequence Diagram
semantic mapping
next
<<Event>>
<<Event>>
Schedule
r
Lift
Door
Move
Stop
next
1: request
<<Object>>
2: up
?
<<Class>>
Lift
causes
Lifts
3: arrived
4: open
causes
<<Object>>
<<Class>>
Door
Doors
next
<<Event>>
<<Event>>
Open
Close
next
next
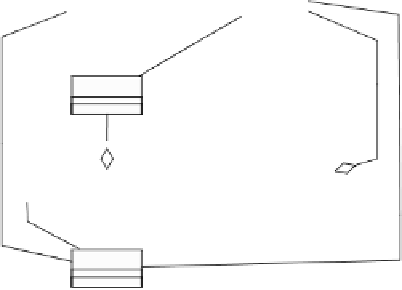
Inference of causality
Sequence Diagram: up
causes
arrived
causes
open
Ontology: Move
next
Stop
next
Open
next
Stop
missing!
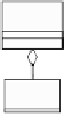
Fig. 3
A sequence diagram and a domain ontology
Meta Model Ontology
Meta Model of
Sequence Diagram
semantic mapping
consume
produce
Function
Data
Data
describe
semantic
mapping
associate
carry
change-from
next
Message
State
Event
?
change-to
receive
send
participate
source
Class
Association
Object
describe
destination
abstraction
semantic mapping
manipulate
Object
describe
Meta Model: Message
carry
Data, Message ? Message
Ontology: Event
associate
Data, Event
next
Event
Next
missing
Fig. 4
Meta model and meta model ontology
figure. We will explain stereotypes attached in classes of the ontology in the next
example of a meta model ontology shown in Fig.
4.
The analyst maps the messages “up” and “open” in the sequence diagram into
Move and Open concepts of the ontology, when developing the diagram, as shown in
Fig.
3.
Suppose that the execution order of message sending in a sequence diagram
is represented with the relationship “causes” between messages. This relationship

























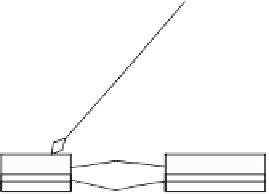












Search WWH ::

Custom Search