Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
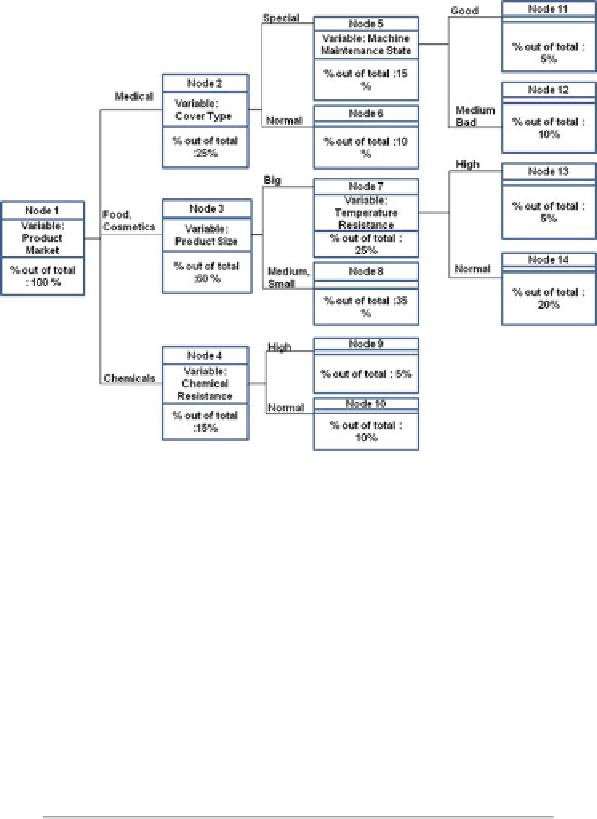
Fig. 3
Context identification decision tree
Ta
b l e 2
Behavioral category distribution for leaf nodes 8, 9, and 13 (in %
)
Leaf node
Category
Path
Termination
13
9
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
1
2
3
Success
Success
Success
Quality problems
Quality problems
Quality problems
13
40
40
3
2
2
10
40
42
3
2
3
7
38
43
4
5
3
Based on Table
2,
the hypothesis that the instances in all the three leaf nodes are
of the same population cannot be rejected, hence condition (a) is satisfied. To check
condition (b), Table
3
shows the distribution of termination states for every path in
the leaf nodes.
Based on Table
3,
paths 1 and 2 lead to significantly different termination states
in leaf node 8 as compared to leaf nodes 13 and 9. Hence, it cannot be considered
in the same context group.
In summary, while the two conditions hold for leaf nodes 9 and 13, they do not
hold for the combination including leaf node 8. Hence, leaf nodes 13 and 9 can
be joined to one context group (instances with big products and resistance to high

Search WWH ::

Custom Search