Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
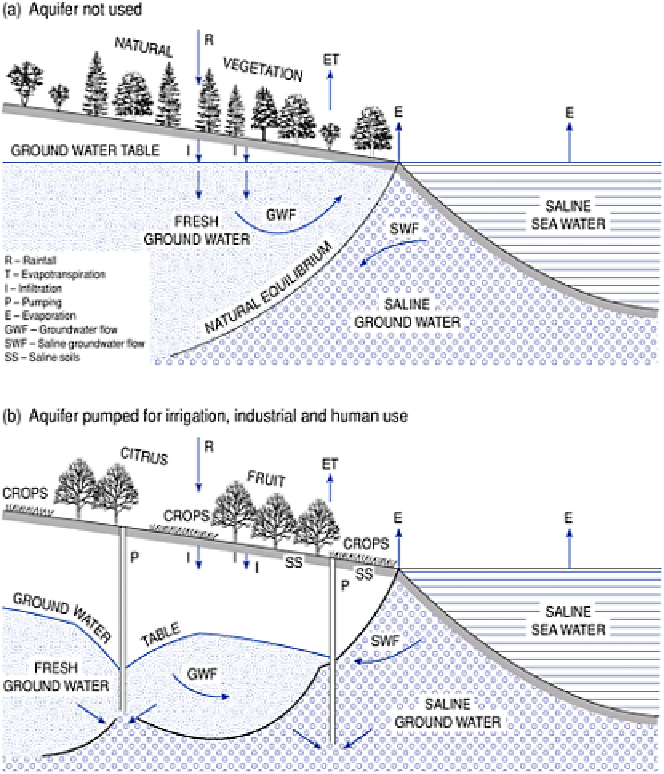
Figure 26.16
The hydrological cycle in a coastal aquifer in
the Mediterranean zone: (a) a non-exploited aquifer, (b) an
aquifer exploited for irrigation, industrial and domestic uses.
areas fresh ground water is in equilibrium pressure with saline ground water.
Pumping of the groundwater resource has drastic consequences (Figure 26.16b). The
groundwater level is lowered as surface run-off is reduced, giving reduced infiltration and
recharge. Under natural conditions the fresh water-saline water interface is at an
equilibrium position; sea water extends under the land not at sea level but at a depth
below sea level equal to about forty times the height of the freshwater table above sea
level. Extracting ground water from coastal aquifers therefore not only lowers water
tables but also causes an intrusion of sea water inland at depth. This extension of saline
ground water further into the aquifer creates a serious problem, and causes salt water to