Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
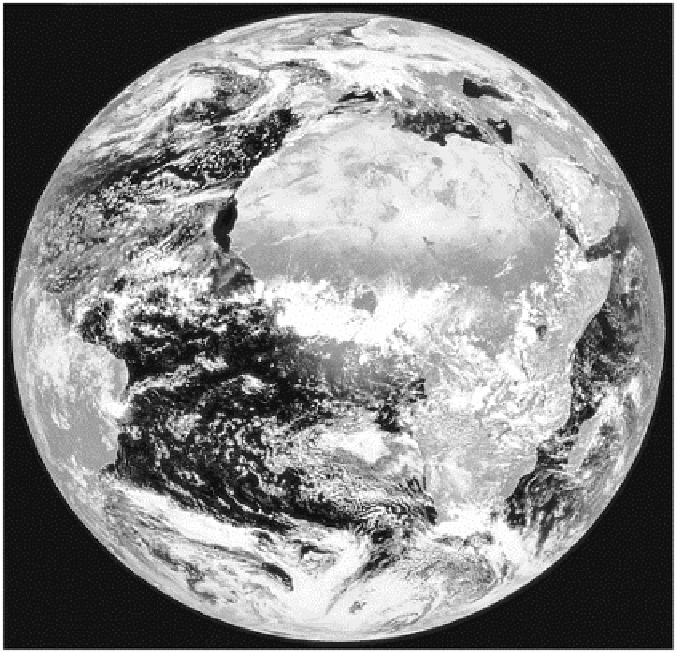
Plate 3.1
A visible waveband Meteosat image on March 17,
2001, showing the variation in reflection (albedo) of different
surfaces. Where cloud-free the oceans stand out as dark, and
the contrast between the vegetated surfaces of West Africa
and the Saharan desert is marked.
Image: courtesy of the NERC Satellite Station, University of
Dundee.
SPATIAL VARIABILITY OF RADIATION EXCHANGES
Earth is a large spheroidal body which spins on an axis tilted at 23½° to the vertical and
has an elliptical orbit around the sun. These factors alone have a considerable influence
on how radiation is distributed at Earth's surface.
Earlier we described the input of solar energy at the top of the atmosphere and how it
was determined by these astronomic controls. Figure 2.12 showed how the radiation
would be distributed at the top of the atmosphere. However, if we look at a map of the