Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
salinity). This global conveyor of heat in the world's oceans will be sensitive to additions
of fresh water to the Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW) and North Atlantic Deep Water
(NADW) through ice-sheet melting (see Chapter 11). The future behaviour of the
oceanographic factor is a major unknown. There is little evidence on how global warming
will affect ocean currents, but thermohaline circulation appears to control the thickness of
the largest ice shelves, and there is the potential for the currents to be altered or even
switched off.
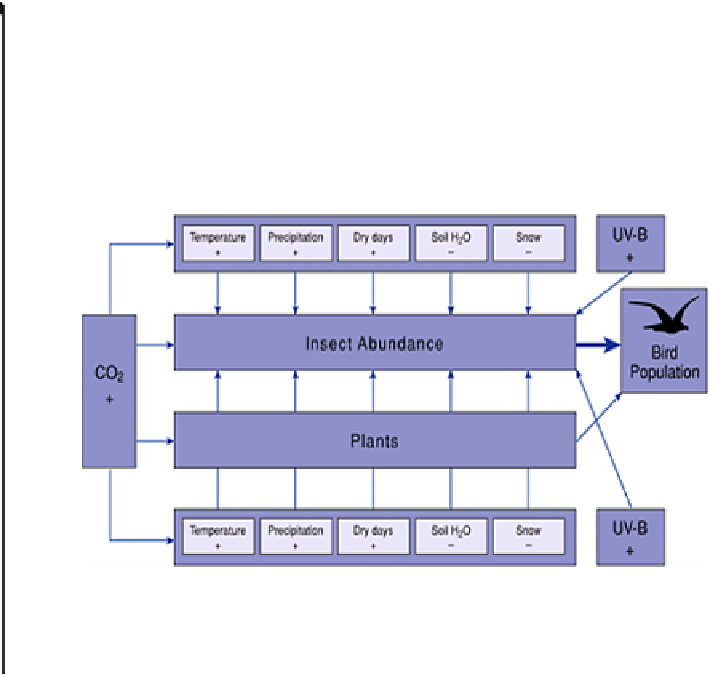
Figure 2
Impacts of increased CO
2
on climate and
bird populations.
data on most Arctic animals. Variability is one indicator of ecosystem stability (see
Chapter 23), and with their high variability Arctic populations appear unstable. An
adverse impact, either through a natural cause (climate, disease, for example) or because
of human action (overhunting or pollution, for example), entails a high probability of
extinction if the impact occurs at the trough of the cycle. Thus musk oxen have been
eliminated from Russia (though now reintroduced from Canada), and the muskox
population of Canada was on the verge of extinction in 1917, when a total ban on hunting
was introduced. Bowhead whales were also on the verge of extinction before protection.
CONSTRUCTION PROBLEMS
One definition of cold regions is that they are places where engineering is complicated by
the natural freezing and thawing of the ground, which significantly increase construction
costs. Permafrost covers more than 50 per cent of the land surface in Canada and Alaska,
and significant parts of Russia and northern Scandinavia. It greatly complicates work on
any engineering construction associated with economic development, e.g. housing,
industrial plant, roads, railways, airstrips or pipelines for oil and natural gas. The term