Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
from
K
and the longer time needed to return to it (lower resilience). System D is the
continual cycle referred to previously (Arctic populations); it is dynamically stable. All
the above trends assume that the perturbations are equally strong. In the real world the
behaviour of ecosystems will depend on the precise nature of the perturbation and on its
magnitude.Table 23.5 lists the major perturbations (disturbances) which affect
ecosystems.
Some perturbations cause very large changes in the abundance of species, like the
severe British winter of 1962-3, which lowered bird populations. Others may involve the
removal of some species, as in the outbreak of Dutch Elm Disease in 1975-85, which
involved a long-term recovery. Perturbations need to be defined in terms of area of
impact and time of impact. For that reason it is difficult to compare widely different
ecosystems, although comparisons should be possible for similar ecosystems.
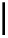
Two approaches to defining stability quantitatively are possible. The first, favoured by
the ecologist MacArthur, uses information theory, in a similar manner to its use in the
definition of diversity (pp. 463-4). Arguing that more ecosystem linkages and a more
even flow of energy along them will give greater stability, one arrives at:
Table 23.4 Definitions of stability
Term
Definition
Units
Stable
Returns to initial equilibrium after a perturbation
n.d.
Resilience
Speed of return to equilibrium after a perturbation
Time
Persistence
Time before variable changed to new value
Time
Resistance
Degree of change after a perturbation
n.d.
Variability
Variance of population densities over time
s.d or c.v.
Notes: n.d., non-
dimensional; s.d., standard deviation; c.v., coefficient of variation.
Figure 23.6
The definition of stability. The behaviour of four
different systems: A, a stable tropical rain forest; B, an
unstable system; C, a boreal coniferous forest, stable but less
so than A; D, a dynamically stable population which cycles.