Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
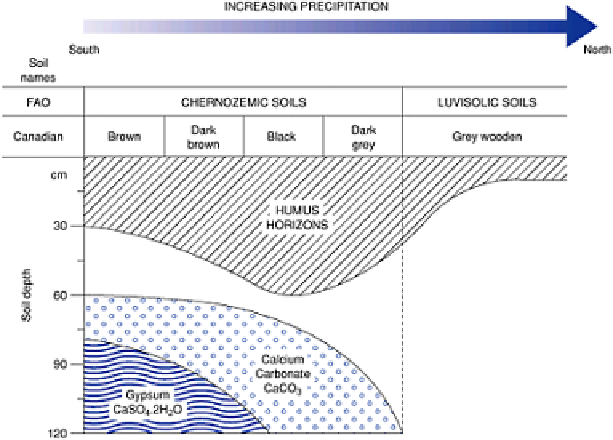
The removal of free calcium carbonate from soils by leaching is called
decalcification
and leads to a lowering of soil pH. In humid regions free calcium salts will be washed out
of the soil profile but as the rainfall decreases in semi-arid and arid regions they may not
be entirely removed but instead be deposited in the subsoil. This is called
calcification
and occurs with calcium carbonate (CaCO
3
) and calcium sulphate (gypsum
CaSO
4
.2H
2
O). Where these accumulate in the lower profiles, calcic (Bk and Ck) and
gypsic (By and Cy) horizons are formed. As gypsum is more soluble than lime, the
gypsic horizon is found below the calcic horizon. It also disappears first from the soil
profile in a sequence of soils from arid to humid regions. The sequence in Figure 19.7
shows these changes taking place along a north-south transect in central Canada as one
moves from a humid to a semi-arid climate (see Colour Plate 20 between pp. 400 and
401).
PODZOLIZATION
Podzols were first named by peasants in the Russian
taiga
, or coniferous forest, who
noticed a distinct white horizon below the surface litter and at depth a black layer.
Believing the black layer to be charcoal from past forest fires, they called the white layer
podzol
or literally 'ash soil'. This is
Figure 19.7
The position of lime and gypsum horizons along
a transect of increasing aridity from south to north in central
Canada.
not, of course, the way in which the soils are formed, but it describes well the pale
surface horizon of
eluviation
(out-washing) overlying the blackish or orange horizon of