Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
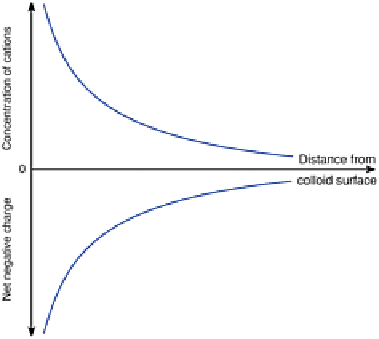
Figure 18.9
How the distribution of adsorbed cations and the
strength of the net negative charge varies with distance from
the surface of a soil colloid.
commonest base cations (Ca, Mg, K, Na) are given, together with those for hydrogen (H).
The total cation exchange capacity is the sum of these five ions, and the percentage base
saturation (% BS) is the proportion of the CEC occupied by these four base cations. The
pH values (pp. 393-6) are directly related to % BS.
ORGANIC COLLOIDS
The values of the cation exchange capacities for clay minerals range from a low of about
5 me 100 g
−1
to a high of about 150 me 100 g
−1
, depending on the type of clay mineral
(Table 18.7). Organic colloids or humic colloids have much higher activity values in the
range 150-300 me 100 g
−1
(Figure 18.10). The reasons for this high activity are not fully
understood, but it appears to derive from the negative charges of phenolic (OH) and acid
carboxyl groups (COOH) which occur in both humic and fulvic acids.
Soil organic matter (SOM) is that fraction of the soil