Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
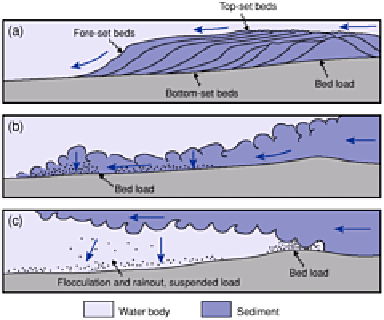
Figure 17.8
Fluvial sediment deposition in marine or
lacustrine basins. Gilbert-type delta formation (a) by rapid
deposition of bed load contrasts with sediment plumes
entering less dense (b) or denser water (c).
Source: Partly after Elliot (1986).
Deltas extend the coastline most obviously where tide and wave energy are low, in
protected shelf seas, and do little to reshape the delta. The modern Mississippi river forms
a classic elongated, fluvially dominated delta where it enters the hurricane-prone, but
otherwise sheltered, Gulf of Mexico. Increasing wave action arrests the delta front nearer
the regional coastline. Transverse bars become more prominent, developing onshore to
form an interrupted barrier coastline (see below) damming tidal lagoons to their rear.
Tide-dominated deltas are subject to tidal inundation and low-tide drainage through the
distributary channel network and surface saltwater flooding of the delta plain. The higher
the tidal range, the more the landward water and sediment fluxes of incoming tides
constrain the seaward development of the delta.
The delta landsystem is a three-dimensional mosaic of individual channel, plain,
lagoon, salt-pan and barrier landforms with wide-ranging sediment calibres. Channel
meandering, storm events and fluctuating sea levels create ever-changing surface
patterns. Delta plain surfaces are also prone to subsidence through the compaction,
dewatering and isostatic depression of sediment under its own weight. Predominantly
low-energy, nutrient-fed environments of the delta plain encourage highly productive
floral and faunal ecosystems. As a result, fossil deltas often contain hydrocarbon
deposits. Modern bioproductivity often encourages high-density but vulnerable human
populations, living at subsistence level, into areas prone to regular and sometimes
disastrous flooding. Storm surges in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta in Bangladesh
claimed 225,000 lives in November 1970 and 138,000 in April 1991.