Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
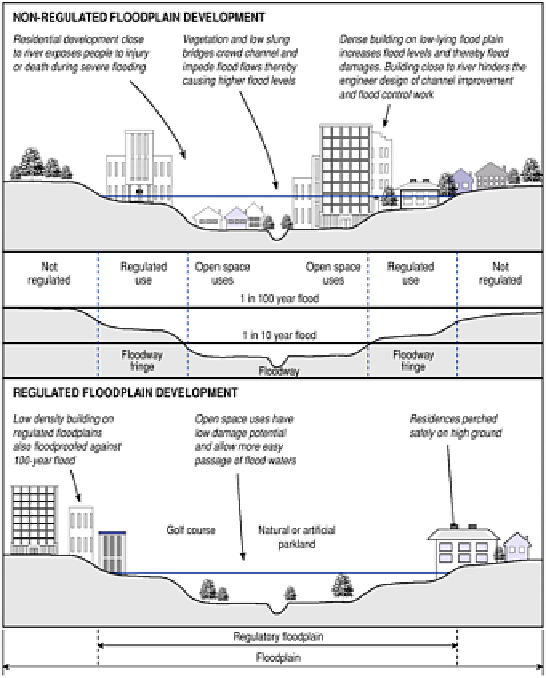
Figure 1
The regulation and zoning of urban flood plain
development (from a New Zealand case, after Newson, 1992).
delivered to channels from adjacent slopes and reworking of unconsolidated fluvial
sediments. Bedrock channels are proof of fluvial erosion and channel incision maintains
potential energy on valley slopes. Despite the great depth and angular profile of many
incised bedrock channels, fluvial erosion is not fully understood. The Colorado river,
over 1·5 km deep in the Grand Canyon (Arizona), is the most celebrated example (Colour
Plate 10 between pp. 272 and 273), but bedrock segments found in most upland rivers
demonstrate its principal processes and effects.
Corrosion
, or the removal of soluble minerals, and the
abrasion
(=
corrasion
) of
particles moving against bedrock have limited impact beyond the smoothing of channel
walls. Corrosion depends on rock susceptibility, water velocity and discharge, but most
dissolved load is probably acquired from pre-channel processes, since water spends
relatively little time in channels. Abrasion depends on bed shear stress, flow turbulence