Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
THE ROCK CYCLE (1) IGNEOUS PROCESSES AND
LANDSYSTEMS
Magma mineralogy and specific temperature/pressure
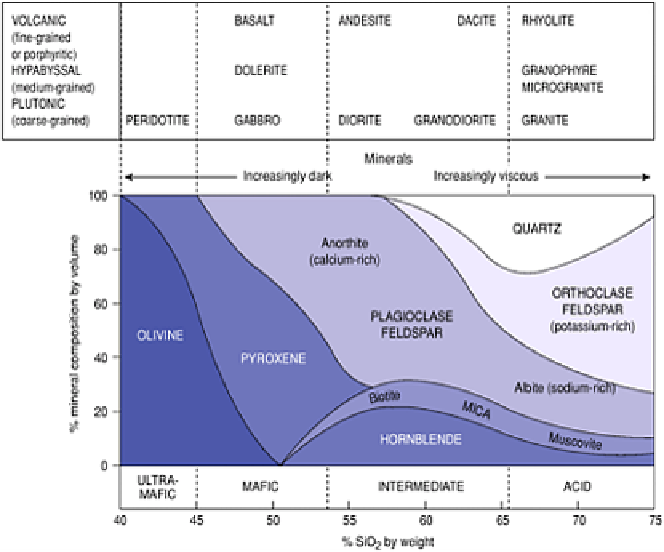
Figure 12.3
Mineral composition, texture, viscosity and
emplacement environment of the more common igneous
rocks. Volcanic rocks are eruptive or extruded at the surface;
hypabyssal and plutonic rocks intrude existing rocks at
intermediate and greater depth.
environments, found at a predictable and restricted range of sites in the global tectonic
framework, determine the style, location and lithology of igneous activity. Magma which
solidifies before reaching the surface is
intrusive
in style and
plutonic
in location; magma
which reaches the surface is
extrusive
in style, with an
effusive
(flowing) or
explosive
(eruptive) nature. The characteristic mineralogy, magma class, texture, viscosity and
surface/ subsurface formation of the principal igneous rocks are identified in Figure 12.3.
These distinctions also extend to the style of eruptive activity and resultant igneous
landforms.