Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
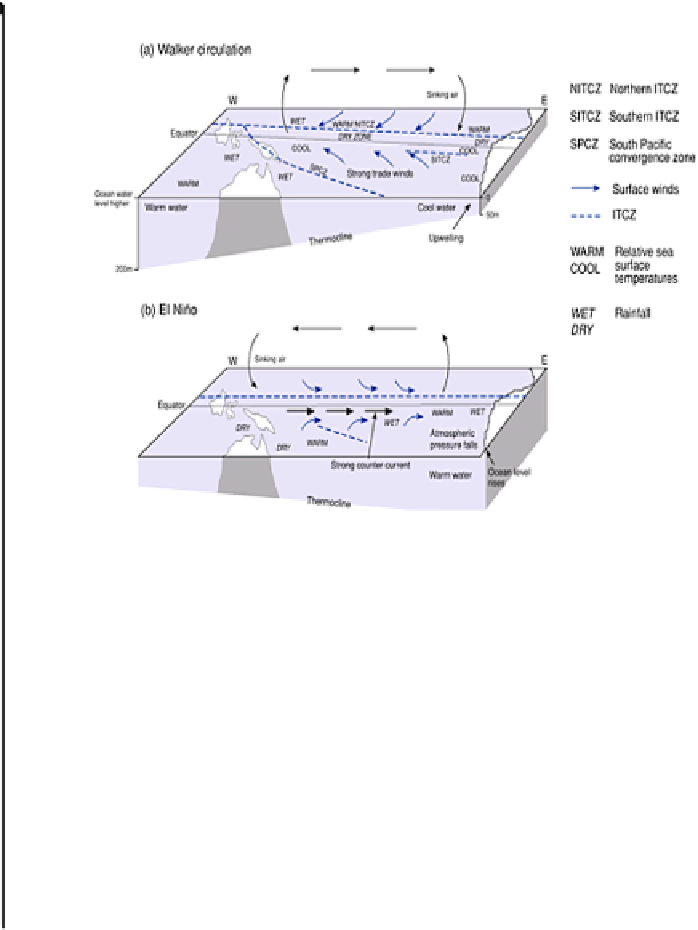
Figure 1
Schematic picture of the South Pacific during the major
phases of ENSO. Note: the vertical scale is greatly exaggerated.
Not only does ENSO have a major regional impact in the Pacific, its influence extends
to other parts of the world through the interaction of pressure, air flow and temperature
effects. During the major El Niño of 1997/8 there were climatic extremes in many parts
of the world. Australia, southern India and southern Africa had major droughts, but the
greatest effects were noted in Indonesia, where extensive forest fires rampaged,
producing vast amounts of smoke pollution. Levels of particulate matter in the air
reached well above the World Health Organization's recommendations and aircraft
flights were affected through poor visibility and air quality. Tropical storms followed
anomalous tracks, reducing rainfall in areas which normally experienced the storms, such
as north-east Australia, and affecting areas outside the usual range, such as Hawaii. In the
northern hemisphere, California suffered major storms as the westerly circulation became
more intense in the north Pacific.