Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
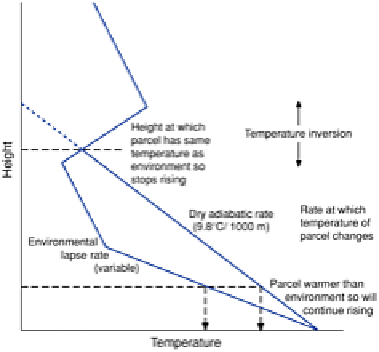
Figure 4.1
Thermal buoyancy of an air parcel. The parcel
will continue to rise as long as it is warmer than the
surrounding air.
of moisture the air contains to the amount of moisture the air could hold when saturated
at that air temperature, expressed as a percentage. Relative humidity may be measured
indirectly from wet-bulb and dry-bulb thermometer readings, using humidity tables.
Evaporation of moisture from the wet bulb leads to cooling which is inversely
proportional to the relative humidity of the air. If the air is saturated, there will be no
evaporation, no cooling and so no difference in temperature between the dry and wet
bulbs. Although frequently used, relative humidity does have the disadvantage of being
temperature-dependent. For example, as air temperature rises relative humidity will fall,
because the air is able to hold more moisture, even though the moisture content of the air
has remained constant. An absolute method of measuring moisture content is to
determine the vapour pressure, which is that part of the total atmospheric pressure exerted
by water vapour. Again it can be obtained indirectly