Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
insertion of dual selective/counter-selective marker into the desired point; 2)
elimination of the marker via
λ
Red-mediated integration of the short dsDNA
fragment containing the mutation of interest flanked with sites homologous to
the appropriate target. Such an approach based on ET-recombination or
λ
Red-
recombination was previously exploited for introduction of the unmarked muta-
tions in E. coli [40,41]. One of the most popular counter-selective markers used
for this purpose is the sacB gene from B. subtilis, whose introduction imparts
sucrose sensitivity to the bacterium.
To create a template for the PCR amplification of the dual selective/counter-
selective marker, cat/sacB, the pRSFPlacsacB plasmid was constructed. The cas-
sette PlacUV5-sacB-cat was amplified with primers containing 36-nt homologies
to the target on their 5'-ends, and integrated into SmaI recognition site located in
hisD gene using SC17(0) harboring pRSFRedkan as a recipient and the cat gene
in the cassette, as the selective marker. A short 170-bp long dsDNA fragment
harboring an appropriate mutation and 82-bp long flanks homologous to the
target region has been constructed (Fig. 2A). The desired modification of bacterial
chromosome (substitution of the artificial XhoI for the native SmaI site) was fi-
nally achieved via the
λ
Red-mediated integration of the obtained DNA fragment
accompanied by elimination of PlacUV5-sacB-cat, using sacB gene for counter-
selection (Fig. 2B). The integrants of interest were found with a rather high fre-
quency (25%) among the clones grown on LB-agar containing 30% sucrose.
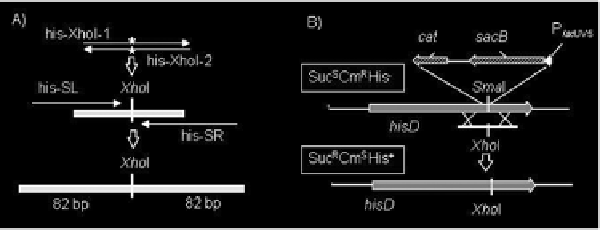
Figure 2.
Construction of the unmarked nucleotide exchange in the P. ananatis hisD gene.
A) Construction of a
dsDNA fragment with appropriate mutation in the center. First, his-XhoI-1 and his-XhoI-2 oligos are annealed
to each other. The nucleotide exchange of interest included in the sequence of his-XhoI-1/his-Xho2 olig is
indicated by asterisks. The resulting dsDNA fragment is then used as DNA-template for PCR-amplification
with his-SL and his-SR oligos. As a result a linear dsDNA fragment, harboring a XhoI restriction site and
82 bp long arms homologous to the target region of hisD gene, was obtained. B) The cassette containing
dual selective/contra-selective marker is integrated into the target point of hisD gene. The constructed in vitro
linear dsDNA fragment or ssDNA harboring appropriate mutation in the center is then integrated into the
chromosome of this strain by the
λ
Red recombination system. As a result, the dual selective/contra-selective
marker is eliminated from the chromosome with simultaneous introduction of the desired mutation into the
hisD gene. This mutation leads to substitution of the native SmaI restriction site by the XhoI restriction site and
restoration of the amino-acid sequence of HisD protein. Integrants are selected as colonies resistant to sucrose.
Such colonies are subsequently tested for Cm sensitivity, ability for growth without histidine and presence of
XhoI restriction site in the target chromosome point.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search