Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
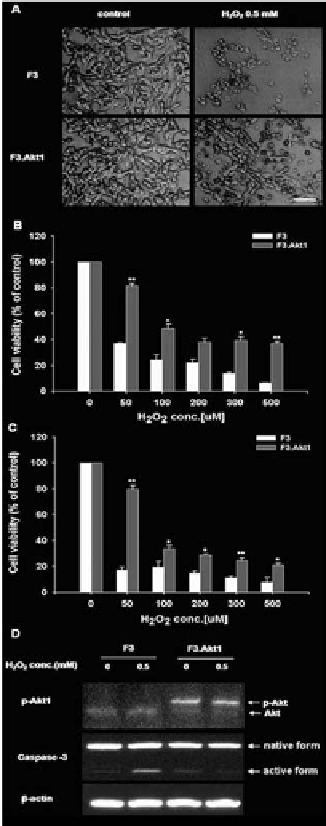
exposure is due mainly from overexpression of Akt1 and its phosphorylation in
F3.Akt1 cell line. And there might be some mediators from Akt1 to caspase-3 in
signal pathway; we could consider that phospho-Akt1 finally inhibits caspase-3
cleavage and activation, thereby provides neuroprotection of the hNSCs.
Figure 2.
Cell viability increases to H2O2-induced oxydative stress conditions and Akt1 phosphorylation in
F3.Akt1 human NSCs.
A: Phase contrast microscopy of F3 and F3.Akt1 human NSCs following exposure to
0.5 mM H2O2 for 6 hr. F3.Akt1 NSCs survived well as compared to the parental F3 NSCs. B and C: F3.Akt1
NSCs were found to show resistance to H
2
O
2
-induced cell death as compared to control parental F3 NSCs at
6 hr (B) and 24 hr (C) respectively. D: Western blot analyses of protein levels of phopho-Akt1 and caspase-3
enzymes in F3 and F3.Akt1 NSCs following H2O2 treatment. F3.Akt1 NSCs showed an increased level of
Akt1 phosphorylation, while the level in activation form of caspase-3 was reduced under the H2O2 treatment
(* p<0.05, ** p<0.001).

Search WWH ::

Custom Search