Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
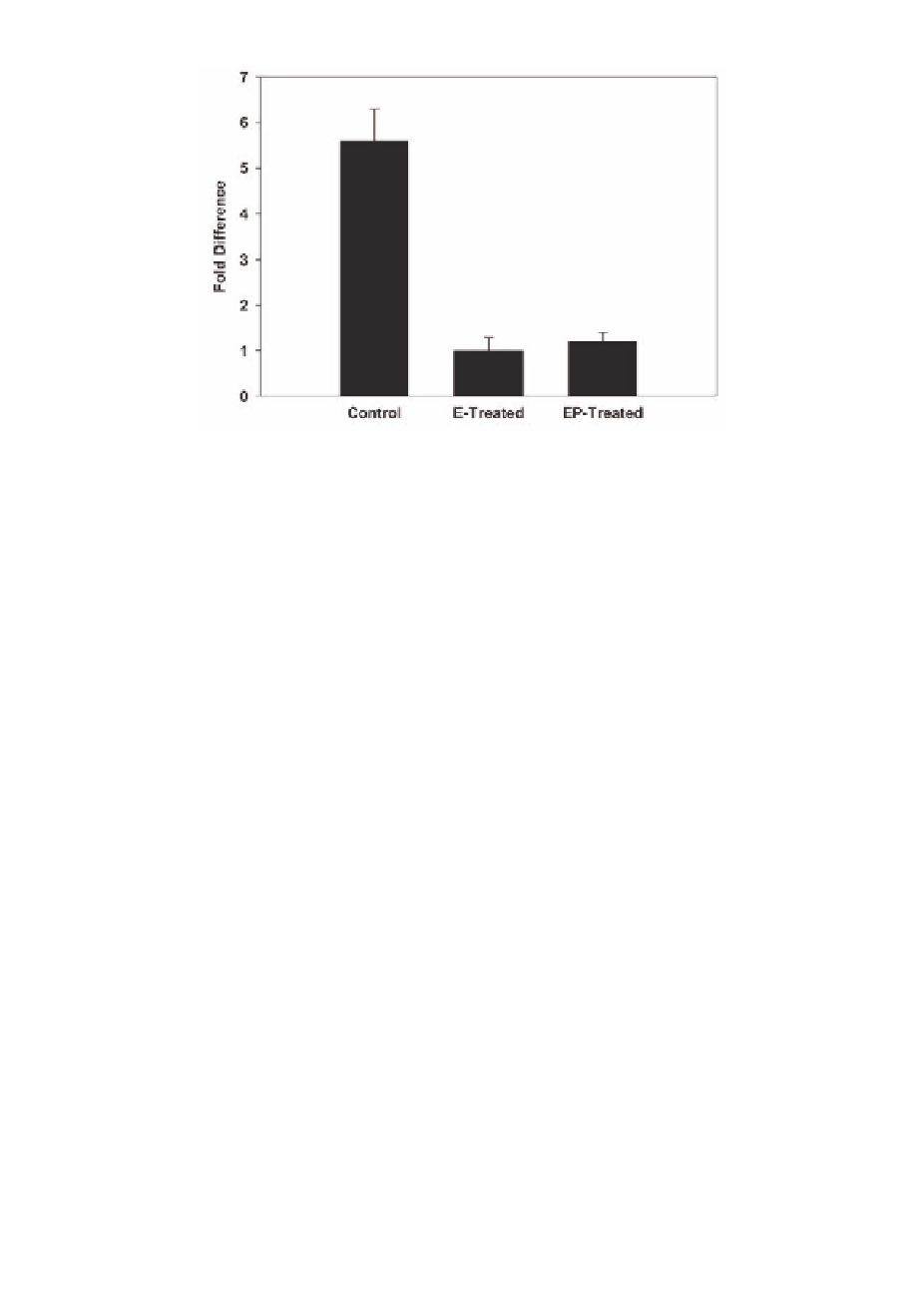
Figure 10.
Cyclin D1 mRNA expression levels in mammary tumors arising in activated Her-2/neu mice. There
was an approximately sixfold increase in the level of cyclin D1 in mammary tumors arising in control mice in
comparison with tumors arising in hormone-treated mice. Results are expressed as means ± SEM.
discussion
The experiments reported here are the first to address the question of whether
short-term hormone treatment can delay tumorigenesis in genetically engineered
models of mammary cancer. All previous experiments, with one exception in
which radiation was used, were performed in rodent models treated with chemical
carcinogen. The results show clearly that a short-term hormone treatment of es-
trogen with or without progesterone can significantly delay tumorigenesis in two
different genetically engineered mouse models. The models differ in fundamental
mechanisms of mammary tumorigenesis. The p53-null epithelium is a model in
which a major tumor suppressor gene is deleted and aneuploidy is a major feature
of the mammary tumors. The tumors arise over a 14-month period and the inci-
dence reaches only 50 to 60% during this period. In contrast, the activated-neu
model represents the overexpression of an oncogene, and tumors arise very rapidly
and with high multiplicity. These results need to be repeated with other geneti-
cally engineered mouse models, such as the BRCA1 and c-myc models, to deter-
mine the wider applicability of this effect of hormones. Conceptually, this result
is important because the genetically engineered models replicate more faithfully
basic features of human breast cancer than do the chemical carcinogen models.
Several results are of general interest. In the p53-null model, the mature gland
as well as the developing (that is, immediately post-pubescent) gland was respon-
sive to the protective state induced by the hormone treatment. This result implies
that there is no unique developmental state of susceptibility. In the MMTV-activated
Search WWH ::

Custom Search